Over the course of his 40-plus years in electrical engineering, Arizona State University's Michael Kozicki has amassed a long list of distinguished credentials.
A spirited storyteller with a crisp Scottish brogue, Kozicki can bring each line of his resume to life such that his career reads less like a series of experiments in a sterile lab and more like a romping adventure in science. But mention dendrites and the animated professor kicks it up a notch, becoming downright rhapsodic.
“It goes way beyond interest,” he readily confesses, laughing. “It’s more like obsession.”
The word dendrite comes from the Greek "dendron," meaning tree. Over the years, dendrites have so enthralled Kozicki that if there’s a branching pattern anywhere in sight, he can spot it: when he flies over the desert and looks down at a network of eroded canyons, when he catches sight of the tree outside his office on the ASU campus, when he gazes at the veins on the back of his own hand.
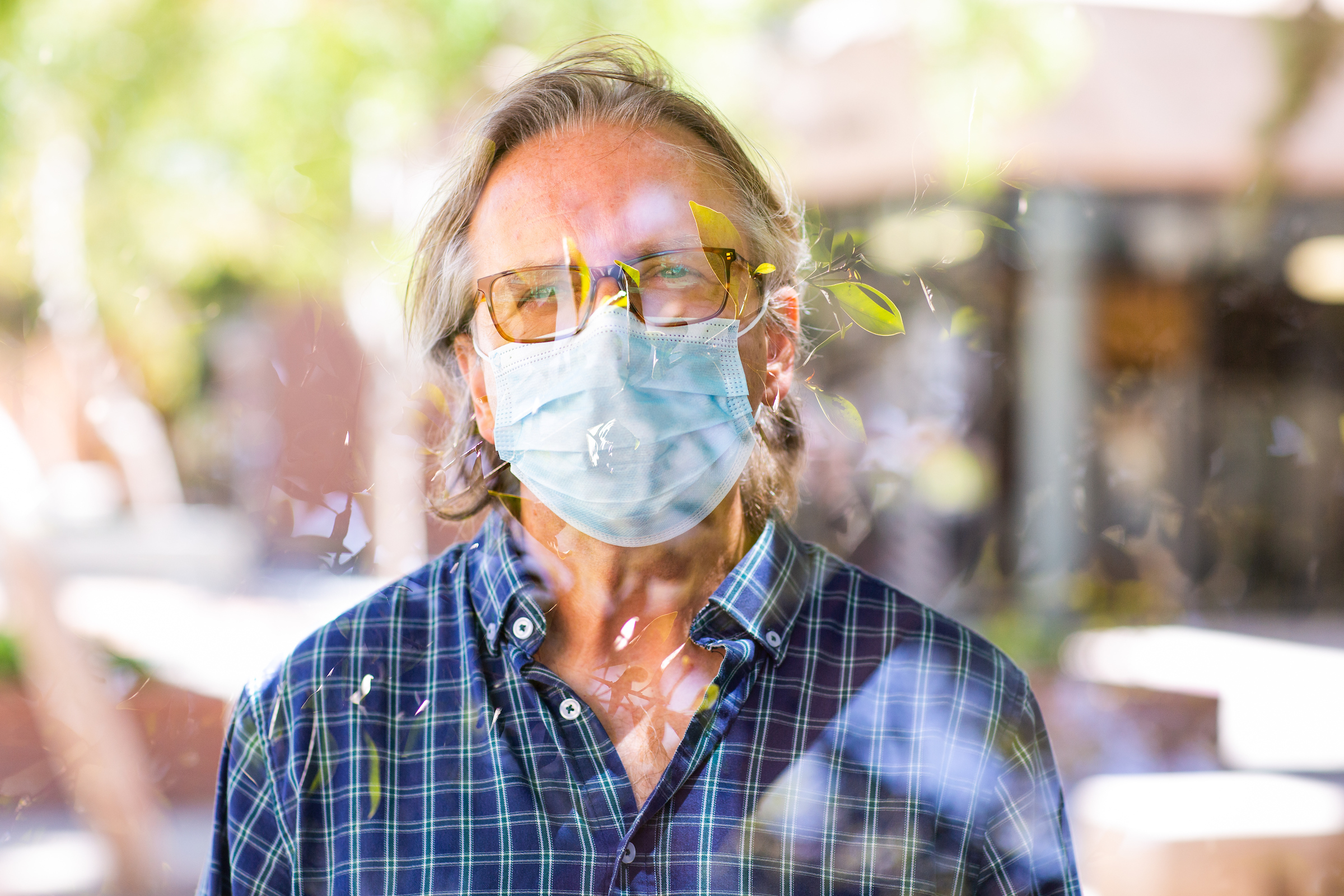
School of Electrical, Computer and Energy Engineering Professor Michael Kozicki poses for a double exposure portrait showing him with leaves and branches, a form of dendrite formations, outside his Tempe campus laboratory on Sept. 3. Photo by Deanna Dent/ASU Now
If it seems like they’re everywhere, Kozicki says, it’s because they are.
“That’s the wacky thing about dendrites. The same branching structures of a tree exist in the bronchial tubes of the lungs, in the connections between the neurons in the brain and even in things like river beds and dry washes where you see these beautiful dendritic patterns caused by water draining under the influence of gravity across tilted planes.
"Mathematicians and physicists call it universality; that is, you can see dendrites whose structures and geometry are incredibly similar in lots of different situations in nature, and yet the processes that created them are ridiculously different,” Kozicki said.
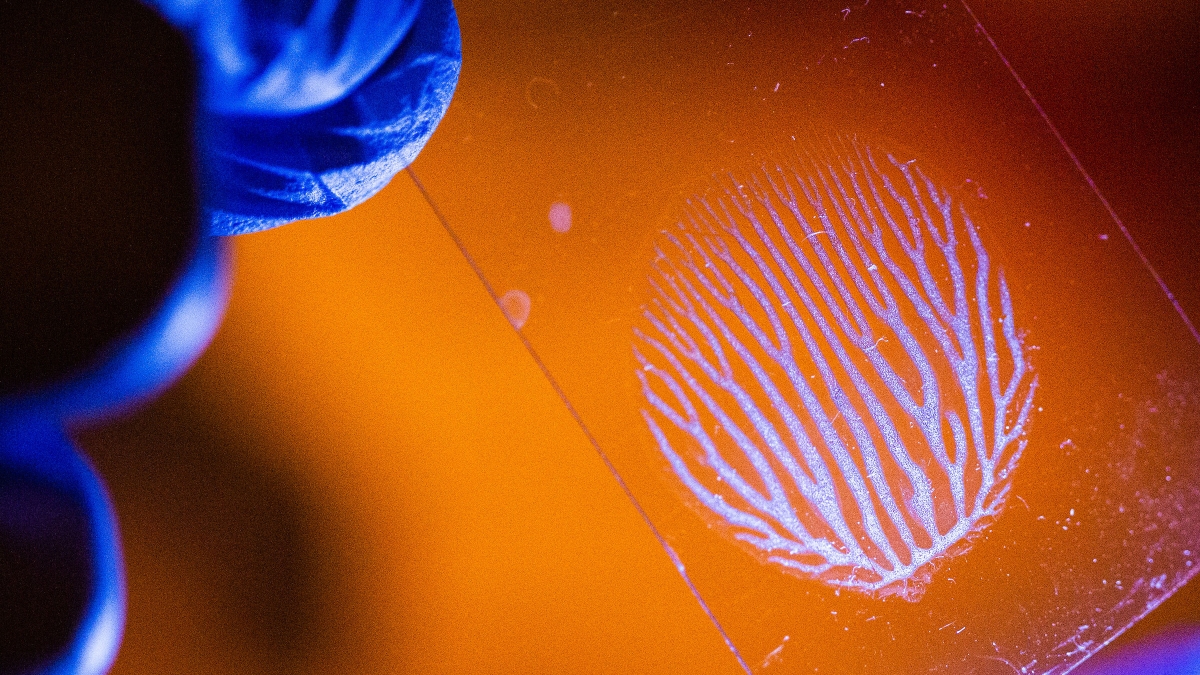
Kozicki first became interested in dendrites some 25 years ago when he began growing them artificially in the lab using an electro-crystallization process. By coincidence, Robby Roberson, a professor in the School of Life Sciences, contacted him around the same time about collaborating on some unorthodox research that happened to involve dendrites as well.
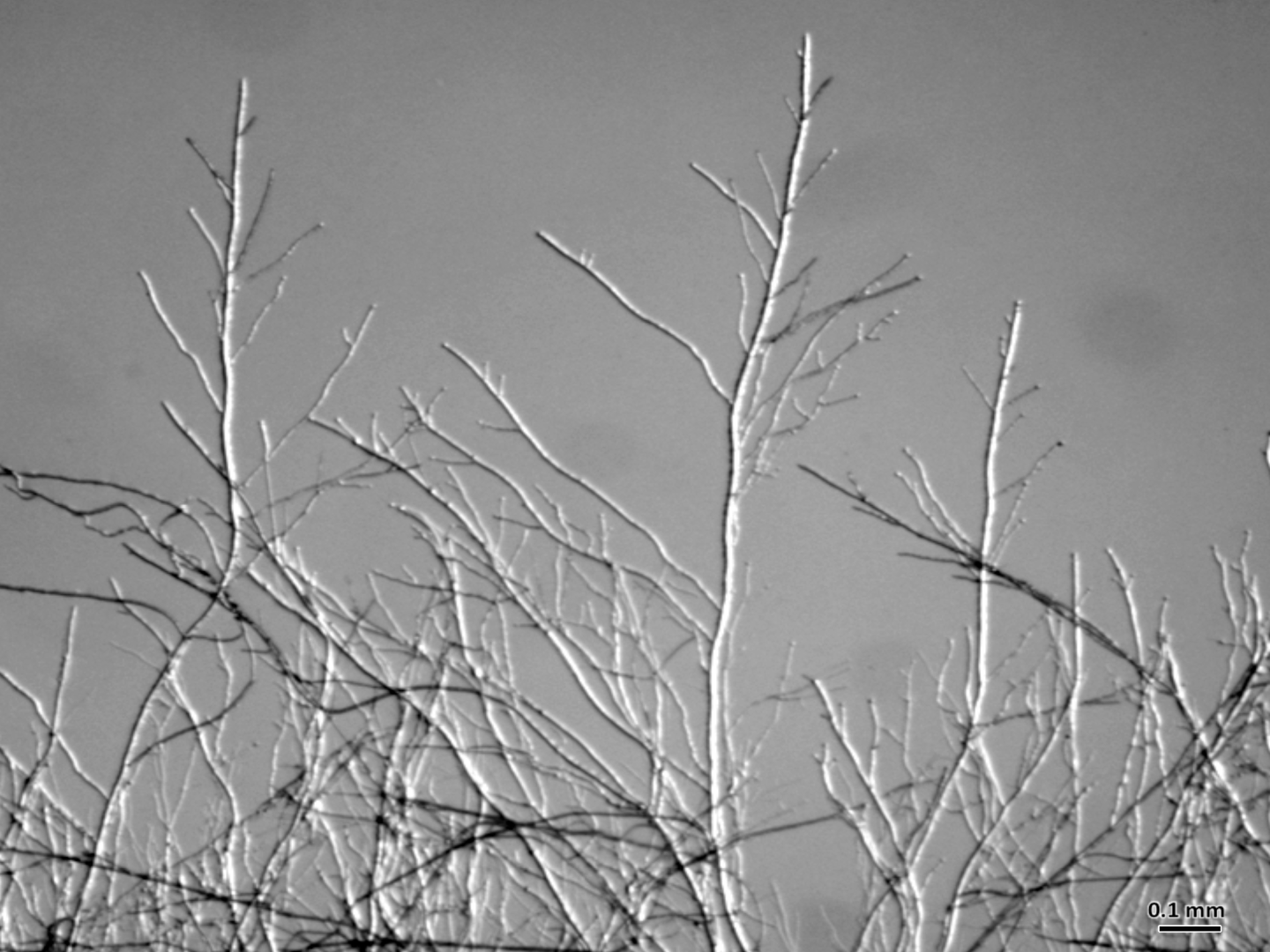
Roberson was studying fungal hyphae — the threadlike structures that fungi produce for gathering nutrients. Hyphae are ubiquitous in nature, winding through the soil or growing onto the surface of living plants and decaying organic matter (think the gray fuzz on the forgotten tomato left to rot at the back of the fridge).
It turns out that hyphae use a variety of wayfinding cues to guide their search for food. In some cases, for example, they can sense the tiny ridges of concentric circles that surround a plant’s breathing pores, or stomata. Guided by these microstructures, the fungal threads can gain entry into the plant through the stomata and spread infection.
Neurospora crassa, a type of red bread mold, displaying hyphal growth and branching. Image courtesy Robby Roberson.
To learn more about how hyphae utilized these and other navigational cues, Kozicki and Roberson inoculated silicon chips that were etched with a series of microstructures found in nature. Then they recorded the response of the hyphae to these artificial prompts, looking especially for any changes in the hyphae’s electrical signals.
The goal of their collaboration was to explore potential new applications in biochemical or physical sensing.
While studying dendrites up close, Kozicki detected a kind of mathematical thriftiness in the branching patterns of these fungal threads. Turns out, the hyphae, like the dendritic patterns of eroded waterways, tree branches and blood vessels, provide an economical means for managing flow.
“The reason why dendrites occur in nature,” he said, “is because nature is always trying to solve the problem of how to minimize the energy of a system. So if you measure all the segments that make up a dendrite, and you add them all up, the total length is shorter than any other mathematical structure that would do the same thing. Dendrites are an optimization function. Nature has optimized the transfer process for moving things like energy, matter or information by creating a structure that has a minimal total distance of all these separate little pieces of the path.”

Robby Roberson
If the dendritic pattern of fungal hyphae served to minimize the energy needed to locate and transport water and nutrients, Kozicki speculated, could it also inspire a structural design for increasing the efficiency of solar cells or electrical-power distribution? To answer these questions, in 2019 he and biologist Roberson once again rolled up their sleeves, thanks to a matching seed grant from ASU’s Biomimicry Center and the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering.
The preliminary modeling results are promising, Kozicki said. Wind-turbine farms, for example, typically use a rectilinear geometry to connect the individual windmills by stubs to one major trunk line that transfers power to the grid.
“Why do we design things at right angles when nature doesn’t?” Kozicki asks.
Instead, he and Roberson measured the number of branches per unit length as well as the angles of the branches in the dendritic pattern of fungal hyphae and used this information to engineer what he calls a dendritic typology.
Models show that using this dendritic typology for the wind-farm design decreased the amount of material needed for running cables while increasing the efficiency of energy transfer into the grid. In the coming year, Kozicki and his team plan to verify the results with colleagues who have an expertise in energy-distribution systems.
This new look at dendrites only deepened Kozicki’s admiration for the power of nature to inspire sustainable innovation.
“Whenever you see a universal phenomenon like dendrites, nature is telling us that this is really useful and it’s useful for a lot of things,” Kozicki said. “I love these kind of revelations. It makes you look in areas you wouldn’t otherwise look. But it’s more than that. Someone once described the feeling that you get when you connect with something big like this as awe. I definitely get that.”
Written by Adelheid Fischer, assistant director of the Biomimicry Center.
Top photo: ASU Professor Michael Kozicki holds examples of dendrite formations created in his laboratory on the Tempe campus. Photo by Deanna Dent/ASU Now
More Science and technology

Swarm science: Oral bacteria move in waves to spread and survive
Swarming behaviors appear everywhere in nature — from schools of fish darting in synchrony to locusts sweeping across landscapes in coordinated waves. On winter evenings, just before dusk, hundreds…

Stuck at the airport and we love it #not
Airports don’t bring out the best in people.Ten years ago, Ashwin Rajadesingan was traveling and had that thought. Today, he is an assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin, but back…

ASU in position to accelerate collaboration between space, semiconductor industries
More than 200 academic, business and government leaders in the space industry converged in Tempe March 19–20 for the third annual Arizona Space Summit, a statewide effort designed to elevate…