Natural cancer killers: ASU Biodesign researcher enhances ability of immune system
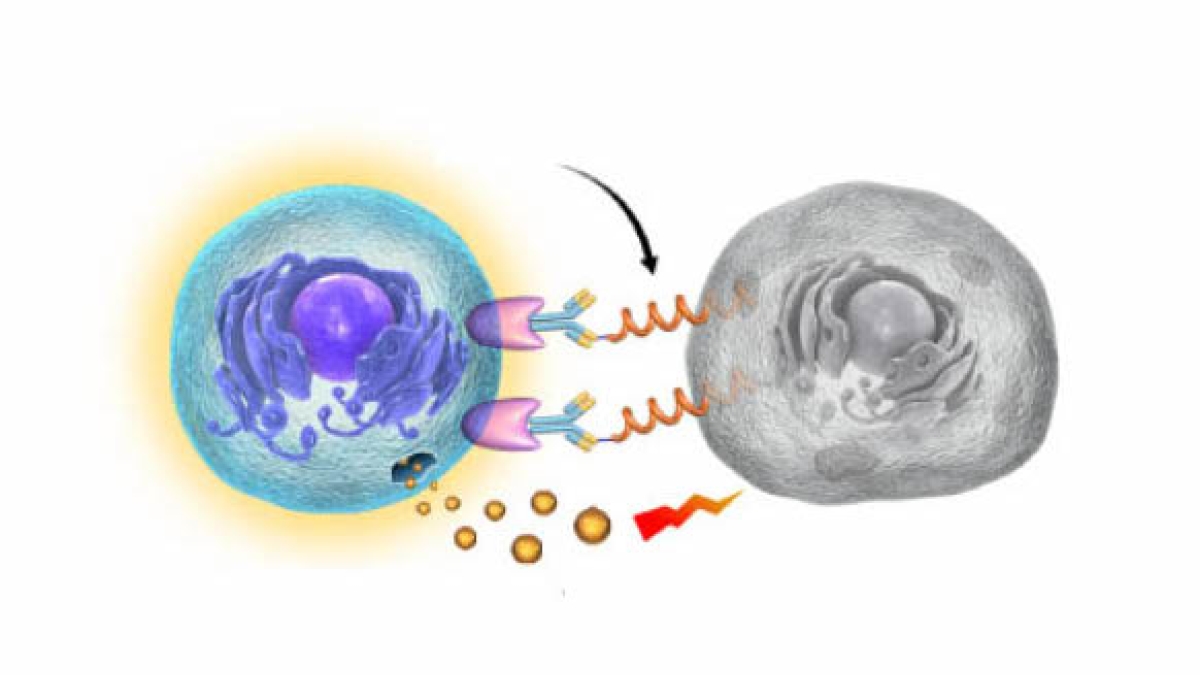
Natural killer cells form a synapse with the hybridized antibody fragments on the tumor cell's surface and induce antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Courtesy of Bo Ning
Cancer remains a leading cause of death globally and is the focus of exhaustive and varied medical research. Many of Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute researchers are working to establish alternative therapies that sidestep the harmful effects of chemotherapy and radiation while improving the success rate for the more difficult-to-treat cancers.
These immunotherapies are innovative treatments that leverage the body’s own defense infrastructure to recognize and destroy diseased cells.
Bo Ning, an assistant research professor in the Biodesign Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics, began a collaboration with the National Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences lab in China to develop new immunotherapies, after beginning his work at Biodesign. Ning initially worked in this lab as a PhD candidate and later initiated the collaboration based on his work there.
Their most recent development in this line of work was published in Advanced Materials, a prestigious peer-reviewed journal covering material science. In the paper, the researchers demonstrate that the immune system’s response — dictated by natural killer cells’ recognition of tumor cells — can be enhanced via the introduction of a pH-sensitive peptide to antibody fragments.
“Our study covers antibody therapies, where you can use cancer marker-specific antibodies to treat certain cancer types,” Ning said. “It’s difficult to develop high-affinity antibodies, but we don’t have to use certain antibodies — we can use just a fragment of antibodies. We conjugated this peptide with an antibody fragment, which could activate natural killer cells.”
In other words, the researchers took the predesigned peptide and hybridized it with an antibody fragment that self-assembled on the tumor cells. This antibody fragment can be recognized by the natural killer cells, which trigger cell death.
The peptide is unique in that it is specific to the low-pH qualities of the tumor microenvironment.
“The cancer tumor microenvironment is low pH, low oxygen, so this is a really good application for the pH-response peptide that does not exist in natural settings,” Ning said. “The function of this peptide is to add a certain marker for natural killer cells that only occurs in low-pH environments.”
This method also sidesteps the challenge of traditional antibody-mediated immunotherapies, which involve the lengthy and laborious process of designing antibodies that can recruit immune cells and trigger tumor cell death.
“An advantage is that we just use a really simple peptide and inject it into the tumor area, and we don’t have to develop new antibodies,” Ning added.
Ning and his fellow researchers hope to expand on this study, exploring the potential for different animal models, cancer cells and lymphocyte-derived immunotherapies.
“We have designed the peptide, but we are in the process of testing it out with different cancer cells in mouse models,” Ning said.
T cells, a type of lymphocyte that binds to foreign peptides presented by infected or cancerous cells and destroys them, are also a potential target for immunotherapies.
T cell therapy takes a patient’s pre-existing T cells and engineers them to attack the specific tumor cells or introduces cells or molecules associated with T cells that further activate an adaptive immune response. Ning hopes to contribute to such therapies by using a strategy like the one he used to activate natural killer cells but for the activation of T cells.
“I am currently working on T cell therapy here at Biodesign, so we will eventually test this technique with T cell activation,” Ning said.
More Science and technology

ASU professor breeds new tomato variety, the 'Desert Dew'
In an era defined by climate volatility and resource scarcity, researchers are developing crops that can survive — and thrive —…

Science meets play: ASU researcher makes developmental science hands-on for families
On a Friday morning at the Edna Vihel Arts Center in Tempe, toddlers dip paint brushes into bright colors, decorating paper…

ASU water polo player defends the goal — and our data
Marie Rudasics is the last line of defense.Six players advance across the pool with a single objective in mind: making sure that…

