Can earthquakes from injected wastewater be predicted?
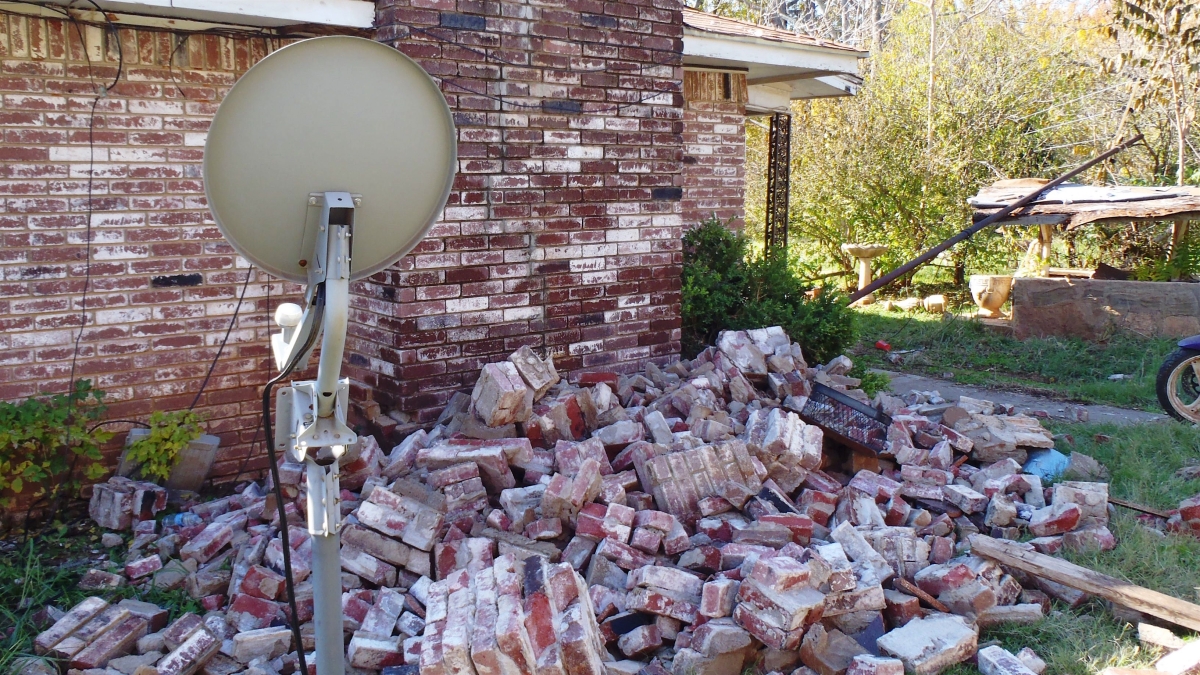

A house in central Oklahoma was damaged by the magnitude 5.6 earthquake on Nov. 6, 2011, which research suggests was caused by wastewater injected into deep disposal wells. ASU scientist Manoochehr Shirzaei has received a Department of Energy grant to develop a method for predicting the size and time of earthquakes from wastewater injection. Photo by Brian Sherrod/US Geological Survey
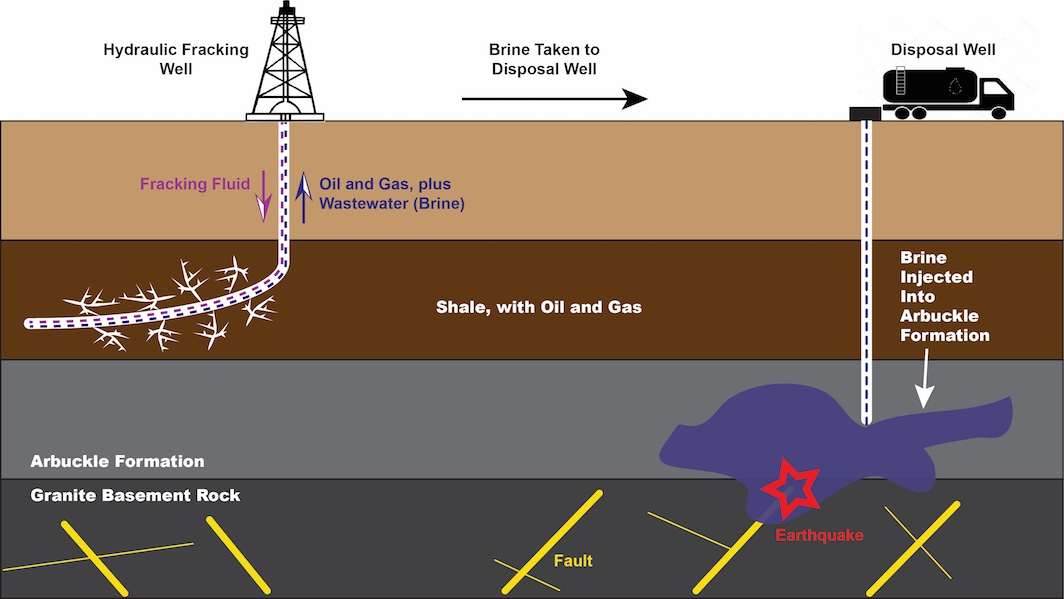
One of the fastest-growing techniques for producing oil and gas today involves widening cracks in hydrocarbon-bearing rock formations underground. The cracks are opened by forcing a mixture of water, sand and chemicals into them in a process commonly called fracking.
The resulting fluid is processed to remove the oil and gas it has freed from the rock, and a wastewater residue called brine is left. The brine, which is toxic, is then disposed of by injecting it into deep layers of the Earth capped with rocks that keep it from reaching the surface.
But the injection process, which is carried out far away from the fracking sites, can induce earthquakes. These may be large enough to damage buildings and other structures at the surface where the brine injection is done.
To gain an understanding of how brine injection causes earthquakes, Arizona State University scientist Manoochehr Shirzaei has received a $1 million grant (over three years) from the U.S. Department of Energy to model the injection process and its subsequent effects.
"Our goal is to find a physics-driven mathematical relationship between the amount of brine injected, its depth, and any effects at the surface," said Shirzaei, an assistant professor in ASU's School of Earth and Space Exploration.
"These effects can include earthquakes and also deformation — uplift — of the ground surface," he said.
First focus: Oklahoma
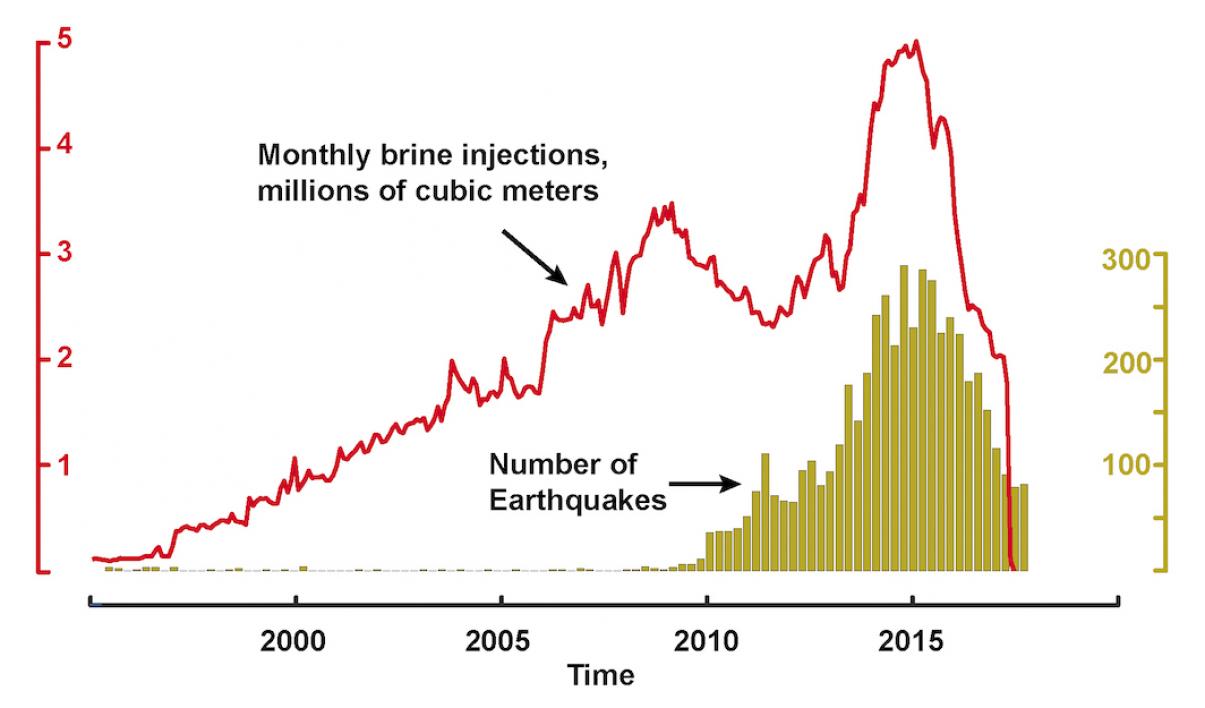
Initially the study will focus on Oklahoma, a state that has been a center for brine injection activities and which has logged a detailed record of seismic events. These include a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in September 2016.
"We will also consider expanding the research to include brine injection sites in Texas, California, Ohio, Kansas, and Colorado," Shirzaei said.
Seismic records are readily accessible for the study from the U.S. Geological Survey, and quantities of injected brines are, by law, made publically available by the companies involved.
A third element in the modeling is to include any deformation of the ground level. This is usually hard to measure because the effects are small and spread over a wide area. However, the use of interferometric synthetic-aperture radar (InSAR) data from orbit allows precise measurement of millimeter-scale uplifts over areas that are miles across.
Shirzaei explains, "We are looking to correlate injected wastewater quantities, measured deformation, and previous seismic activity to develop a model that can predict the likely effects of brine injection activity in a given area."
Because extraction of oil and gas is so important to a modern economy, Shirzaei expects the study will benefit a variety of stakeholders.
"The general public is the most important because they may be exposed to potential injury and damage," he said. The list also includes oil and gas producers, brine injection companies and geothermal energy providers.
"In addition, we expect the study will benefit land-management, regulatory, and permitting agencies," Shirzaei said. "Plus emergency managers and responders, building owners, insurers, mortgage holders and research scientists."
More Science and technology

ASU to host 2 new 51 Pegasi b Fellows, cementing leadership in exoplanet research
Arizona State University continues its rapid rise in planetary astronomy, welcoming two new 51 Pegasi b Fellows to its exoplanet…

ASU students win big at homeland security design challenge
By Cynthia GerberArizona State University students took home five prizes — including two first-place victories — from this year’s…

Swarm science: Oral bacteria move in waves to spread and survive
Swarming behaviors appear everywhere in nature — from schools of fish darting in synchrony to locusts sweeping across landscapes…