Imagine being able to see something as tiny as a single molecule, which is a billion times smaller than a meter. Now imagine trying to keep track of it in motion, something even super-resolution microscopy struggles to do.
The ability to track and study processes at the level of single molecules could greatly change our understanding of complex biological systems and lead to new scientific and technological advances. For example, that level of precision could aid in the development of treatments for diseases like cancer, where targeted drug delivery — which requires tracking the binding and unbinding of individual drug molecules to their targets to understand the kinetics and efficacy of potential treatments — can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Thanks to the research of Arizona State University Professor Steve Pressé, we’re one step closer to that reality.
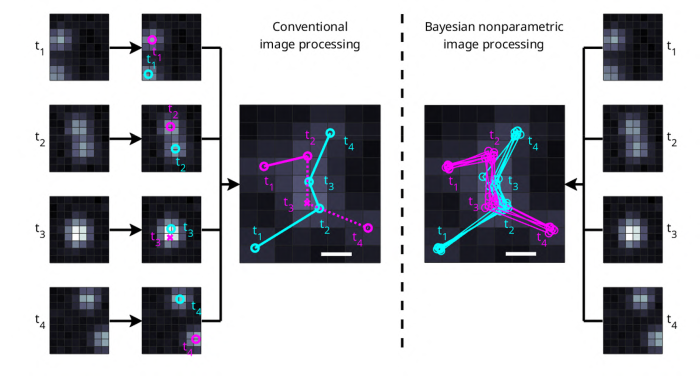
Pressé — a researcher in ASU’s School of Molecular Sciences and in the Biodesign Center for Mechanisms of Evolution — and his team have created a computational system to gather information from individual photons, or light particles, emitted by single molecules. This technique allows them to track molecules in motion with high precision, providing scientists with a unique ability to observe chemical, physical and biological processes as they happen.
Their paper, "BNP-Track: A framework for superresolved tracking," explains how they capture the emitted light and use advanced algorithms to analyze each photon detected. This process helps them accurately locate each molecule and separate them from background noise or other molecules that might move in and out of focus quickly. This method allows researchers to determine the paths of molecules, even when they move too fast for traditional cameras to capture clearly.
“While we can describe to students the effects of chemical bond rearrangements involved in chemical reactions, we cannot visualize bonds rearranging directly by electrons hopping around. As such, a lot of chemistry and physics is hard to understand and remains abstract,” said Pressé, a professor in ASU’s School of Molecular Sciences. “Thus, we explain concepts through equations and diagrams. To some extent, the same is true of biology — we can describe the nanoscopic world of single molecules and what it might look like in action inside a cell, but often this is deduced from frozen snapshots or molecules in extreme isolation. Here, we try to tease out every bit of information we can from every photon in order to look at macromolecules in action.”
In cell biology, this capability could allow scientists to closely examine processes inside cells, like how proteins move within cell membranes, how cells transmit signals and how the cell's internal structure (the cytoskeleton) changes in normal, crowded environments where many molecules interact. Understanding these details is essential for learning how cells respond to their surroundings at a molecular level.
This technology has significant implications for medicine. By understanding the mechanisms of drug interactions at the molecular level, researchers can design more effective therapies with fewer side effects.
The continued development of these techniques promises to uncover new aspects of molecular behavior and drive innovations in multiple fields.
More University news

ASU President Crow, 'NeoBio' honored at international celebration of innovation
ASU President Michael Crow and NeoBio, the university’s groundbreaking effort to revolutionize biology education, were among the big winners at the Edison Awards, a global celebration of game-…

‘The time to change the future is now’
More than two decades ago, Arizona State University reimagined higher education by evolving into a university focused on inclusion rather than exclusivity and combining broad access and excellence…

3 ASU students earn Goldwater Scholarships for STEM research excellence
Three Arizona State University students have been named Goldwater Scholars for 2025, placing them among the nation’s most promising undergraduates pursuing research careers in science, engineering…