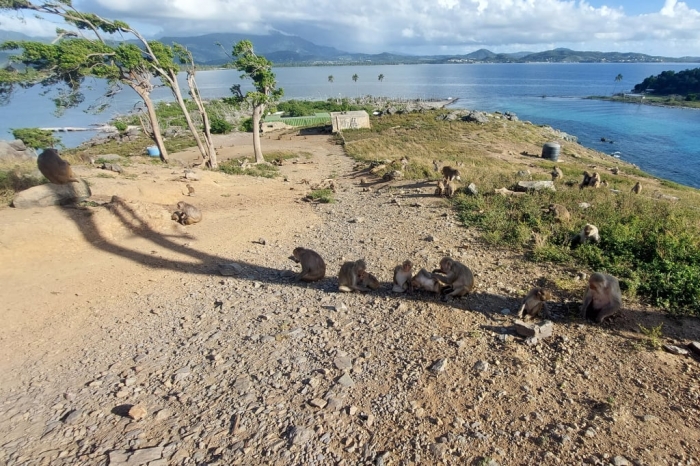
Hurricane changed 'rules of the game' on Monkey Island to foster more cooperation
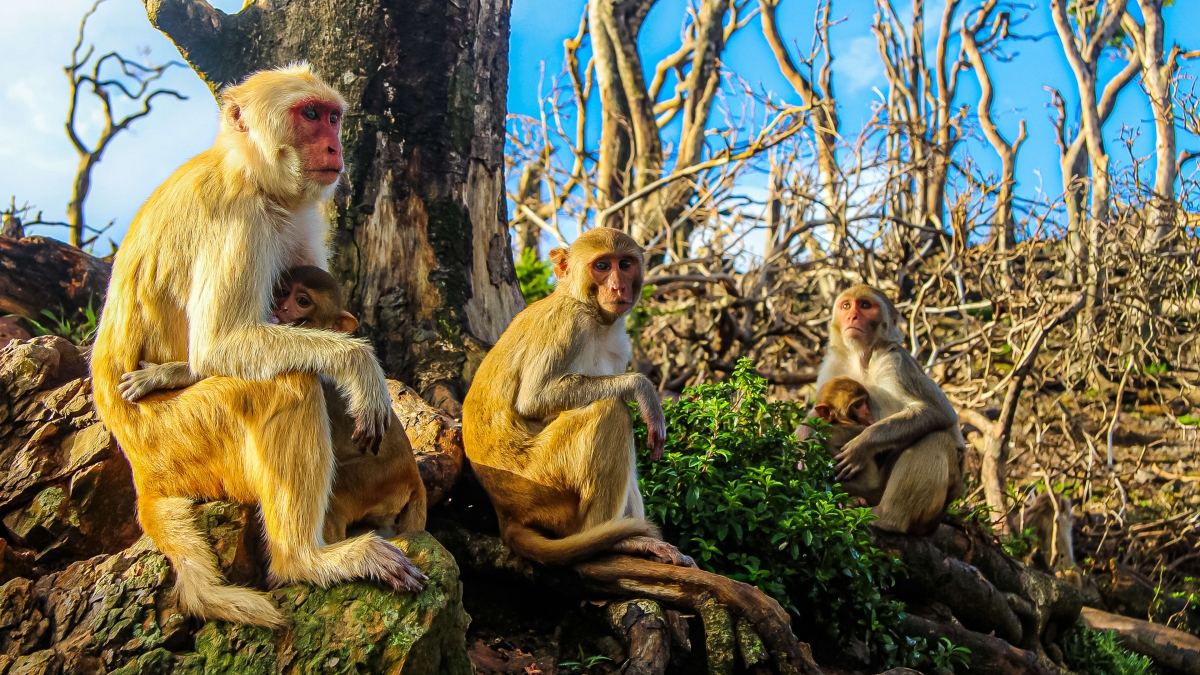

Five years after Hurricane Maria, a monkey society has altered the evolutionary benefits of tolerating others and sharing shade — giving a survival advantage to more tolerant macaques. Photo courtesy of Lauren Brant/University of Exeter
In 2017, Hurricane Maria became the largest catastrophe in the history of Puerto Rico, killing over 3,000 people, knocking out power to nearly all of the island and causing more than $100 billion in damages.
The hurricane also destroyed 63% of the vegetation on Cayo Santiago, a small island off the coast of Puerto Rico known as Monkey Island, which is home to about 1,800 rhesus macaque monkeys.
Remarkably, only 2.75% of the macaque population died in the immediate aftermath of the storm.
In a new study on the monkeys, led by scientists at Exeter University and the University of Pennsylvania, in collaboration with Arizona State University and New York University, researchers found that the storm damage has altered the evolutionary benefits of tolerating others and sharing shade — giving a survival advantage to more tolerant macaques.
The studyStudy funders included the National Institutes of Health, the European Research Council, the National Science Foundation and the Royal Society. has garnered the cover of the prestigious journal Science.
'A Goldilocks research system'
Cayo Santiago has been home to an isolated, free-roaming population of rhesus macaques since 1938. The island serves as a natural laboratory with decades of data, which study co-author Noah Snyder-Mackler describes as “a Goldilocks research system — the perfect mix of the wild and the lab — with a complex social environment where we’re able to pair rich behavioral data with detailed physiological data.”
A 2022 study of monkeys on Cayo Santiago found that survivors of weather-related disasters may have accelerated aging, “with immune systems that looked like (they had) aged an extra two years,” Snyder-Mackler said. “What we are trying to do right now is look at what makes some of these individuals more resilient to the effects of the hurricane.”
Even now, five years after the catastrophe, the tree cover remains far below pre-hurricane levels and — in this hot part of the world — that makes shade a scarce and precious resource for the macaques.
"In response to the drastic changes caused by the hurricane, macaques persistently increased tolerance and decreased aggression towards each other," said lead author Camille Testard, from the University of Pennsylvania and now a junior fellow at Harvard.
"This enabled more macaques to access scarce shade, which is critical for survival."
Testard added: "We examined 10 years of data on the strength and number of macaques' social ties, before and after the hurricane. Before the hurricane, tolerating others had no impact on risk of death. Afterwards, macaques that displayed more than average social tolerance — and were therefore better able to share shade — were 42% less likely to die than those that were less tolerant."
This represents a sudden change in "selection pressure" — the evolutionary benefits or costs of different traits or behaviors.
Changing 'the rules of the game'
Social behavior was assessed by recording aggression and how often individuals were seen sitting together.
"Macaques aren't the best at sharing resources — be they food or shade. They are well known to live in an aggressive, highly competitive society," said Lauren Brent, senior author and professor from the University of Exeter. "But in the heat caused by ecological changes, often around 40 degrees Celsius (104F), the macaques had to share space or die.
"In effect, the hurricane changed the rules of the game in the monkeys' society."
What this study shows, Brent said, is that "for group-living animals, social relationships may allow them to cope with disturbances in the environment, including human-induced climate change."
"We were surprised the macaques' social behavior was so flexible, making them resilient to this environmental change, but some species may not display this same flexibility," Brent added.
Additionally, Testard said, "To access shade, they need to tolerate — and be tolerated by — others, and we found that this tolerance spills over into other daily interactions."
Ultimately, the hope is that the lessons learned from the latest macaque study can also be used to help humans better adapt to weather-related and similar catastrophes.
“The people in Puerto Rico sort of gelled and increased their support of one another in the face of this event,” Snyder-Mackler said. “Given the strong similarity between these monkeys and us, we know that a lot of the work that we are doing and the things that the monkeys might do to be more resilient to this might be translatable to us and might provide ways for us to intervene and help buffer against the negative effects of these traumatic events.”
More Health and medicine

80 years of pioneering speech and hearing services for the community
Over 80 years ago, in 1937, the first course in communication disorders, Speech Correction, was offered at Arizona State University. As additional courses were added and programs in speech…

First 2 degree offerings from ASU Health available in fall 2025
Editor’s note: This story is featured in the 2024 year in review.The first degree offerings from ASU Health will help students find jobs in the modernized health care system.The one-…
ASU study uses new biomaterials for wound healing
A minor cut often heals within days, vanishing without a trace. Yet, wound healing and tissue repair are complex biological processes, revealing the body’s remarkable regenerative capacity.In a new…


