Earliest adorned female infant burial in Europe significant in understanding evolution of personhood

The mouth of the Arma Veirana cave, a site in the Ligurian mountains of northwestern Italy.
Ten thousand years ago, just after the last Ice Age, a group of hunter-gatherers buried an infant girl in a cave in what is now Italy. They entombed her with a rich selection of their treasured beads and pendants, and an eagle-owl talon, signaling their grief and showing that even the youngest females were recognized as full persons in their society.
The excavations and analysis of the discovery are published this week in Nature Scientific Reports and offer insight into the early Mesolithic period, from which few recorded burials are known.
Claudine Gravel-Miguel, postdoctoral researcher with the Institute of Human Origins at Arizona State University and co-author on the paper, performed the analysis of the ornaments, which includes over 60 pierced shell beads and four shell pendants.
Mortuary practices offer a window into the worldviews and social structure of past societies. Child funerary treatment provides important insights into who was considered a person and afforded the attributes of an individual self, moral agency and eligibility for group membership. The seemingly “egalitarian” funerary treatment of this infant female, whom the team nicknamed “Neve,” shows that as early as 10,000 years ago in Western Europe, even the youngest females were recognized as full persons in their society.
“The evolution and development of how early humans buried their dead as revealed in the archaeological record has enormous cultural significance,” said Jamie Hodgkins, ASU doctoral graduate and paleoanthropologist at the University of Colorado Denver.
The excavation
Arma Veirana, a cave in the Ligurian pre-Alps of northwestern Italy, is a popular spot for local families to visit. Looters also discovered the site, and their digging exposed the late Pleistocene tools that drew researchers to the area.
The research team started surveying the site in 2015 and discovered the remains during the last week of the 2017 field season. The team of project coordinators includes Italian collaborators Fabio Negrino from the University of Genoa and Stefano Benazzi from the University of Bologna, as well as researchers from the University of Montreal, Washington University, University of Ferrara, University of Tubingen and ASU Institute of Human Origins.
The first two excavation seasons were spent near the mouth of the cave, exposing stratigraphic layers that contained tools over 50,000 years old typically associated with Neandertals in Europe (Mousterian tools). They also found the remains of ancient meals such as the cut-marked bones of wild boars and elk, and bits of charred fat. In addition, they found stone tools that were much more recent and that had likely been eroding from deeper inside the cave. To better understand the stratigraphy of the cave and document its occupation history, the team opened new sections further inside the cave in 2017. As the team explored this new section, they began to unearth pierced shell beads, which Hodgkins examined more carefully back in the lab.
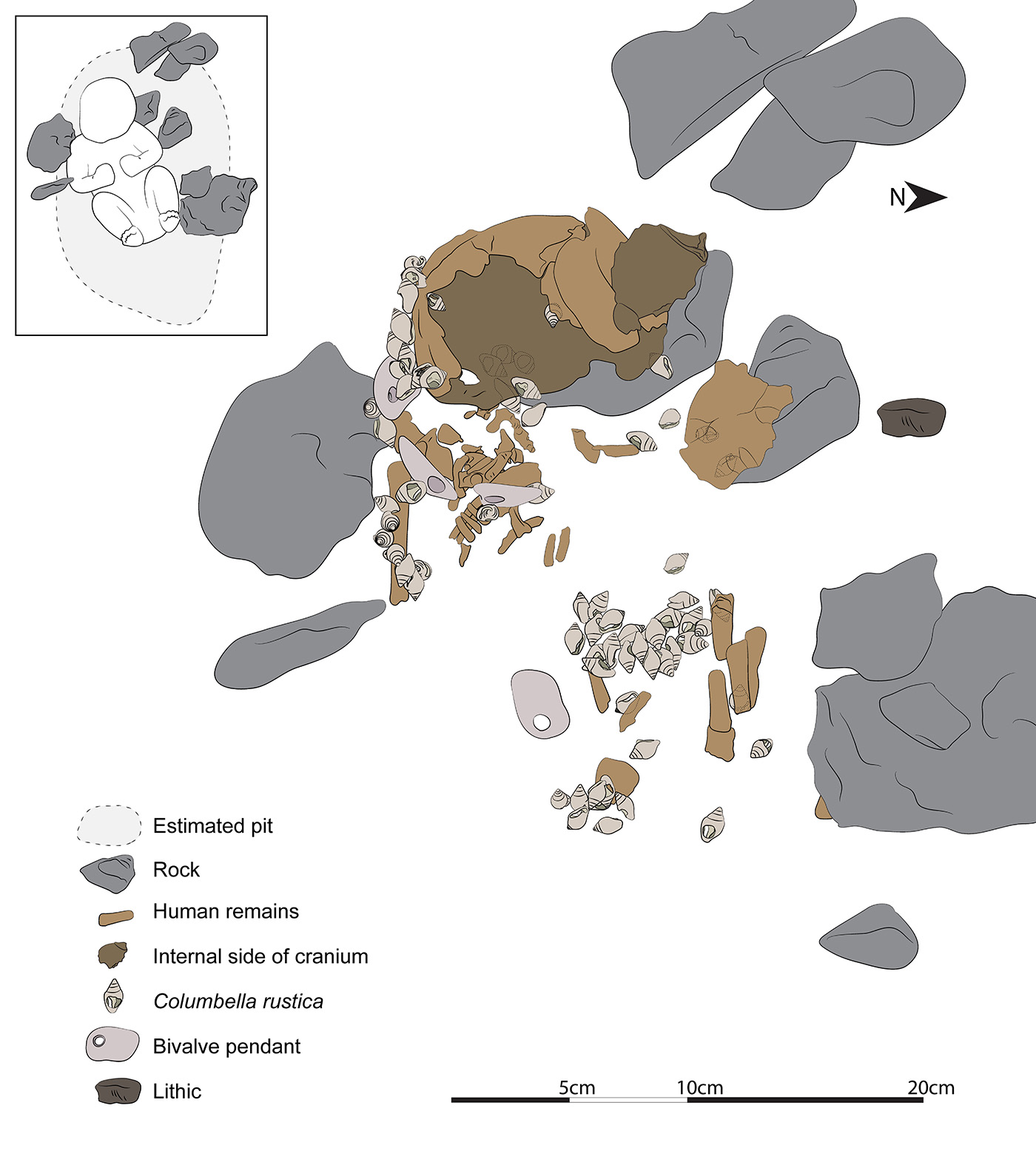
Illustration showing the placement of beads and shells along with the cranium. Image by Claudine Gravel-Miguel
A few days after they found the first bead, one of the excavators uncovered a small piece of the infant’s cranial vault.
“I was excavating in the adjacent square and remember looking over and thinking, ‘That’s a weird bone,’” Gravel-Miguel said. “It quickly became clear that not only we were looking at a human cranium, but that it was also of a very young individual. It was an emotional day.”
Using dental tools and a small paint brush, researchers spent that week and the following field season to carefully expose the whole skeleton, which was adorned with articulated lines of pierced shell beads.
“The excavation techniques are state-of-the-art and leave no doubt to the associations of the materials with the skeleton,” said Curtis Marean, who was not involved in the study. Marean is associate director of the Institute of Human Origins and Foundation Professor with the School of Human Evolution and Social Change.
Important changes in human prehistory
In a series of analyses coordinated across multiple institutions and numerous experts, the team uncovered critical details about the ancient burial. Radiocarbon dating determined that the child lived 10,000 years ago, and amelogenin protein analysis and ancient DNA revealed that the infant was a female belonging to a lineage of European women known as the U5b2b haplogroup.
“There’s a decent record of human burials before around 14,000 years ago,” Hodgkins said. “But the latest Upper Paleolithic period and earliest part of the Mesolithic are more poorly known when it comes to funerary practices. Infant burials are especially rare, so Neve adds important information to help fill this gap.”
“The Mesolithic is particularly interesting,” said co-author Caley Orr, ASU doctoral graduate and paleoanthropologist and anatomist at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. “It followed the end of the final Ice Age and represents the last period in Europe when hunting and gathering was the primary way of making a living. So, it’s a really important time period for understanding human prehistory.”
Detailed virtual histology, or study of the tissue and structure, of the infant’s teeth showed that she died 40 to 50 days after birth and that she experienced stress that briefly halted the growth of her teeth 47 days and 28 days before she was born. Carbon and nitrogen analyses of the teeth revealed that the baby’s mother had been nourishing the infant in her womb on a land-based diet.
The child as a member of the community
Gravel-Miguel performed an analysis of the ornaments adorning the infant, which demonstrated the care invested in each piece and showed that many of the ornaments exhibited wear that proves they were passed down to the child from group members. The details of this research — along with further results — are the focus of a separate article, currently under review.
Citing a similar burial of two infants dating to 11,500 years ago at Upward Sun River, Alaska, Hodgkins said the funerary treatment of Neve suggests that the recognition of infant females as full persons has deep origins in a common ancestral culture that was shared by peoples who migrated into Europe and those who migrated to North America. Or it may have arisen in parallel in populations across the planet.
The research, excavation and analysis were made possible with funding from The Wenner-Gren Foundation, Leakey Foundation, National Geographic Society Waitt Program, Hyde Family Foundations, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme, and the Max Planck Society.
Article: “An infant burial from Arma Veirana in northwestern Italy provides insights into funerary practices and female personhood in early Mesolithic Europe,” Jamie Hodgkins, et al. Nature Scientific Reports.
More Science and technology

Breakthrough copper alloy achieves unprecedented high-temperature performance
A team of researchers from Arizona State University, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Lehigh University and Louisiana State…

4 ASU researchers named senior members of the National Academy of Inventors
The National Academy of Inventors recently named four Arizona State University researchers as senior members to the prestigious…

Transforming Arizona’s highways for a smoother drive
Imagine you’re driving down a smooth stretch of road. Your tires have firm traction. There are no potholes you need to swerve to…

