General public sees government science advisers through political lens, ASU researcher finds

Image courtesy of iStock.
What people think of the scientists who advise the federal government partially depends on their own political persuasion and where the scientists work, according to new findings published this week by an Arizona State University researcher. The study highlights the risk of politicizing scientific advice given to government agencies.
Caitlin Drummond, an assistant professor at Arizona State University’s School of Human Evolution and Social Change, led the research, which explores the public perception of scientific groups aiding federal decision-makers. The work was completed while Drummond was a postdoctoral researcher at the Erb Institute at the University of Michigan.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Drummond’s research asked if people’s political persuasion made a difference in their overall trust in a United States Environmental Protection Agency science advisory board composed of academic- versus industry-affiliated scientists.
The study follows a 2017 rule change disqualifying scientists with EPA grant funds from serving on its advisory board. Since then, industry scientists have replaced some academic scientists on the board. The current board composition is about evenly split between academic and nonacademic scientists. Academic scientists are employed by a university while industry scientists are employed by a consulting firm, corporation, or other organization.
Understanding public perception
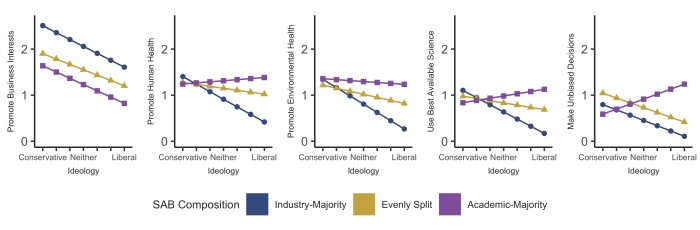
The findings indicated academic-majority boards tended to be viewed as most likely to make evidence-based decisions and promote human and environmental health by all participants except the most conservative. Board composition had less influence on conservative participants’ perceptions, but both liberals and conservatives thought industry-majority boards would be more likely to promote business interests.
Boards with an evenly-split composition tended to be viewed somewhere in between the industry- and academic-majority boards, although people identifying as strongly conservative thought an evenly-split board would be most likely to make unbiased recommendations.
Participants were first asked to consider a randomly-assigned board composition. The compositions included a majority of industry scientists, a majority of academic scientists and an evenly-split board.
Participants were then asked how likely they thought the board would be to promote business interests, promote human health, promote environmental health, use the best available science and make unbiased decisions. Later in the study, participants identified their political affiliation on a seven-point scale ranging from conservative to liberal.
“Our findings suggest that there's a potential for politicization of science advisory board recommendations,” Drummond said. “Science advisory board members apply their values in the form of assumptions and judgments throughout the process of evaluating the relevant science and then making recommendations. Our findings highlight the potential for political disagreements over the values being applied in EPA decision-making.”
As a powerful federal agency, the EPA influences almost all environment-related regulations, including those on foreign and domestic production, clean air and water, and construction and transportation. Its decisions can impact citizens daily.
Applying values and increased transparency
“Many people, including myself, when I started this project, might be unfamiliar with the idea of a science advisory board, but they are commonly deployed, not just by the EPA, but across different agencies and in private industry,” Drummond said. “Advisory boards inform decisions that do eventually impact us in many different areas of life.”
Because people often do not know the reasoning behind decisions made at the federal level, Drummond notes that transparency in the advisory board member selection process may help people better understand what values are applied in decision-making. The authors recommend more transparency, both in how new members are invited onto the science advisory board and how members leave the board.
Drummond’s educational background is in decision science, psychology and economics. Her research seeks to better understand people’s behavior surrounding scientific information, and how science can be communicated effectively.
Other contributing authors to the paper include Sara Goto Gray and Kaitlin Raimi of the University of Michigan, and former EPA science advisory board members Joseph Árvai of the University of Southern California and Robyn Wilson of Ohio State University.
“Public perceptions of federal science advisory boards depend on their composition,” is available via open access from the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
More Law, journalism and politics
Can elections results be counted quickly yet reliably?
Election results that are released as quickly as the public demands but are reliable enough to earn wide acceptance may not always be possible.At least that's what a bipartisan panel of elections…
Spring break trip to Hawaiʻi provides insight into Indigenous law
A group of Arizona State University law students spent a week in Hawaiʻi for spring break. And while they did take in some of the sites, sounds and tastes of the tropical destination, the trip…

LA journalists and officials gather to connect and salute fire coverage
Recognition of Los Angeles-area media coverage of the region’s January wildfires was the primary message as hundreds gathered at ASU California Center Broadway for an annual convening of journalists…