TRAPPIST-1 planets provide clues to the nature of habitable worlds
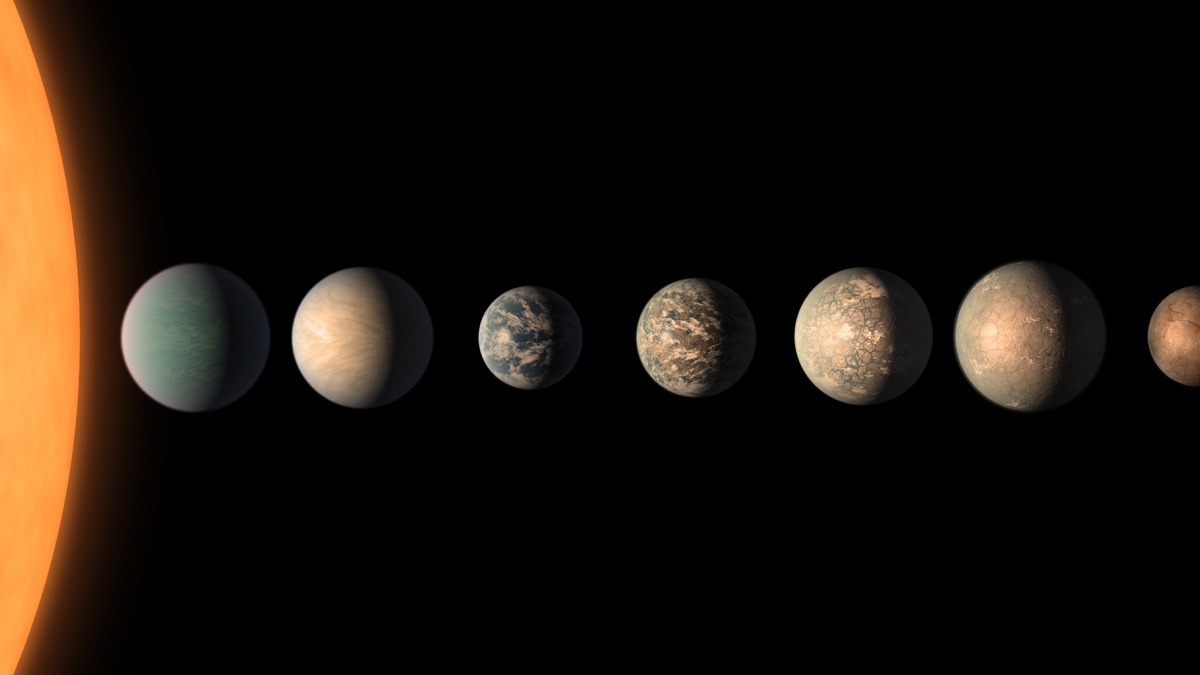

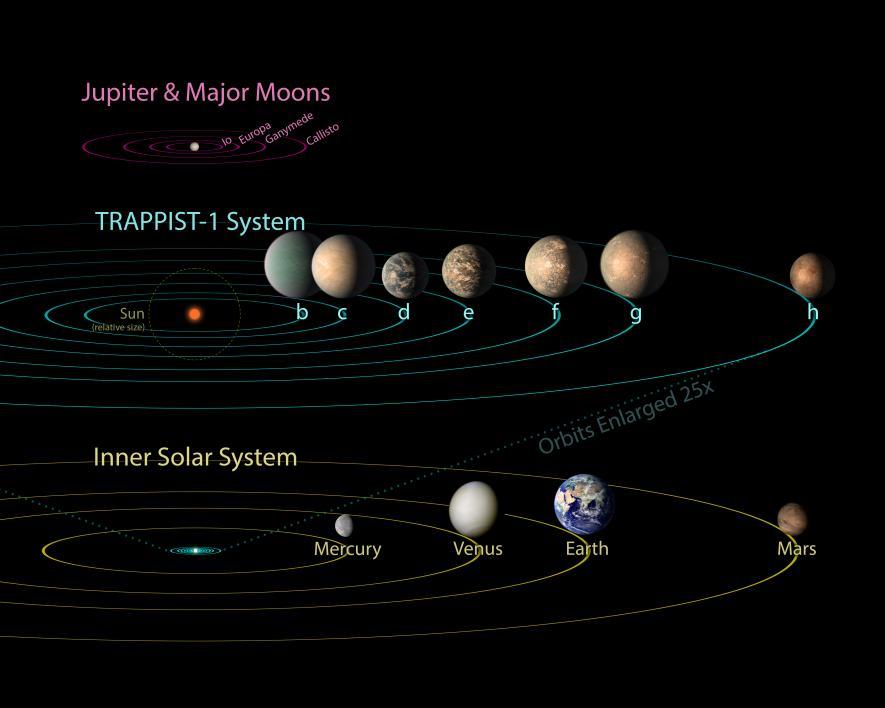
Artist's concept shows what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about the planets' diameters, masses and distances from the host star, as of February 2018. Credit: NASA/JPL- Caltech
TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool red dwarf star that is slightly larger, but much more massive, than the planet Jupiter, located about 40 light-years from the sun in the constellation Aquarius.
Among planetary systems, TRAPPIST-1 is of particular interest because seven planets have been detected orbiting this star, a larger number of planets than have been than detected in any other exoplanetary system. In addition, all of the TRAPPIST-1 planets are Earth-sized and terrestrial, making them an ideal focus of study for planet formation and potential habitability.
ASU scientists Cayman Unterborn, Steven Desch and Alejandro Lorenzo of the School of Earth and Space Exploration, with Natalie Hinkel of Vanderbilt University, have been studying these planets for habitability, specifically related to water composition. Their findings have been recently published in Nature Astronomy.
The calculations equal water
The TRAPPIST-1 planets are curiously light. From their measured mass and volume, all of this system’s planets are less dense than rock. On many other, similarly low-density worlds, it is thought that this less-dense component consists of atmospheric gasses.
“But the TRAPPIST-1 planets are too small in mass to hold onto enough gas to make up the density deficit,” geoscientist Unterborn explained. “Even if they were able to hold onto the gas, the amount needed to make up the density deficit would make the planet much puffier than we see.”
So scientists studying this planetary system have determined that the low-density component must be something else that is abundant: water. This has been predicted before, and possibly even seen on larger planets like GJ1214b, so the interdisciplinary ASU-Vanderbilt team, comprised of geoscientists and astrophysicists, set out to determine just how much water could be present on these Earth-sized planets and how and where the planets may have formed.
But how much is there?
To determine the composition of the TRAPPIST-1 planets, the team used a unique software package, developed by Unterborn and Lorenzo, that uses state-of-the-art mineral physics calculators. The software, called ExoPlex, allowed the team to combine all of the available information about the TRAPPIST-1 system, including the chemical makeup of the star, rather than being limited to just the mass and radius of individual planets.
Much of the data used by the team to determine composition was collected from a dataset called the Hypatia Catalog, developed by contributing author Hinkel. This catalog merges data on the stellar abundances of stars near to our sun, from over 150 literature sources, into a massive repository.
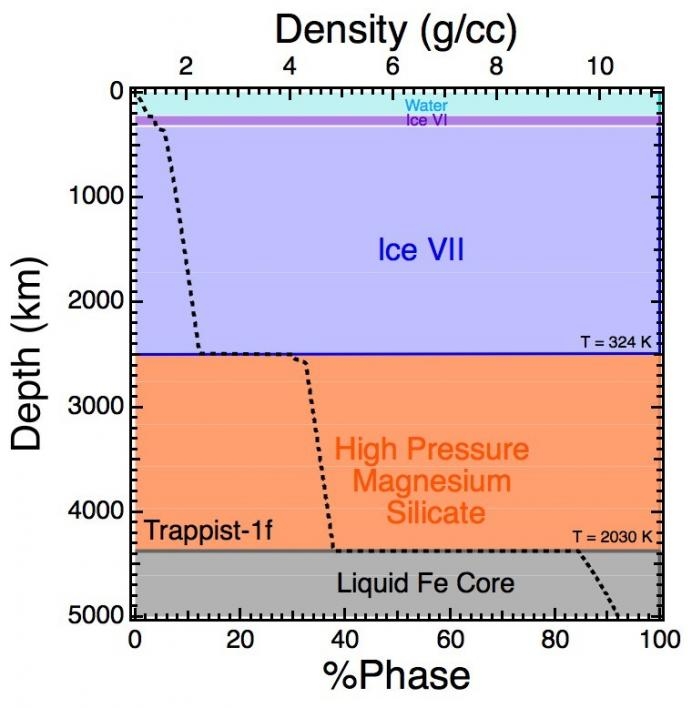
What they found through their analyses was that the relatively “dry” inner planets (“b” and “c”) were consistent with having less than 15 percent water by mass (for comparison, Earth is 0.02 percent water by mass). The outer planets (“f” and “g”) were consistent with having more than 50 percent water by mass. This equates to the water of hundreds of Earth-oceans. The masses of the TRAPPIST-1 planets continue to be refined, so these proportions must be considered estimates for now, but the general trends seem clear.
“What we are seeing for the first time are Earth-sized planets that have a lot of water or ice on them,” said Steven Desch, ASU astrophysicist and contributing author.
But the researchers also found that the ice-rich TRAPPIST-1 planets are much closer to their host star than the ice line. The “ice line” in any solar system, including TRAPPIST-1’s, is the distance from the star beyond which water exists as ice and can be accreted into a planet; inside the ice line water exists as vapor and will not be accreted. Through their analyses, the team determined that the TRAPPIST-1 planets must have formed much farther from their star, beyond the ice line, and migrated in to their current orbits close to the host star.
There are many clues that planets in this system and others have undergone substantial inward migration, but this study is the first to use composition to bolster the case for migration. What’s more, knowing which planets formed inside and outside of the ice line allowed the team to quantify for the first time how much migration took place.
Because stars like TRAPPIST-1 are brightest right after they form and gradually dim thereafter, the ice line tends to move in over time, like the boundary between dry ground and snow-covered ground around a dying campfire on a snowy night. The exact distances the planets migrated inward depends on when they formed.
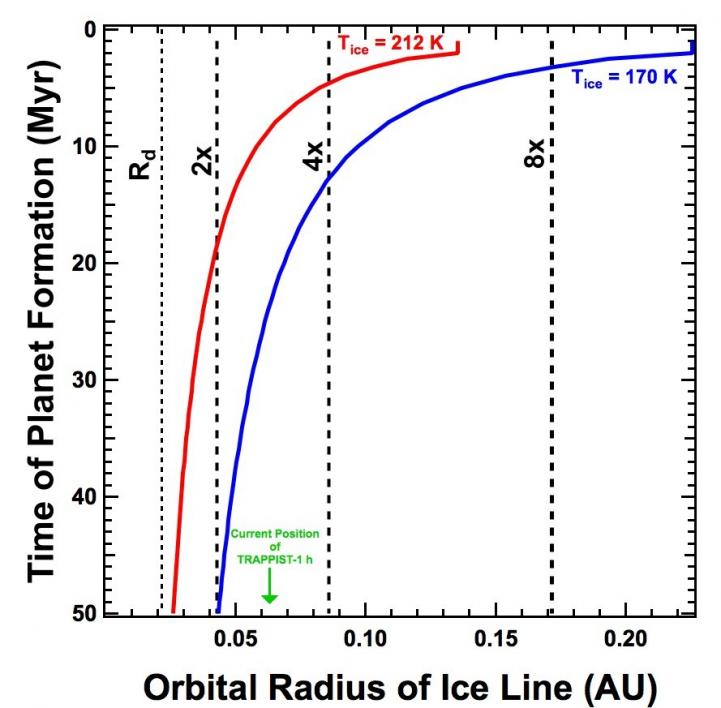
“The earlier the planets formed,” Desch said, “the farther away from the star they needed to have formed to have so much ice.” But for reasonable assumptions about how long planets take to form, the TRAPPIST-1 planets must have migrated inward from at least twice as far away as they are now.
This graph shows the minimum starting distances of the ice-rich TRAPPIST-1 planets (especially f and g) from their star (horizontal axis) as a function of how quickly they formed after their host star was born (vertical axis). The blue line represents a model where water condenses to ice at 170 K, as in our solar system's planet-forming disk. The red line applies to water condensing to ice at 212 K, appropriate to the TRAPPIST-1 disk. If planets formed quickly, they must have formed farther away (and migrated in a greater distance) to contain significant ice. Because TRAPPIST-1 dims over time, if the planets formed later, they could have formed closer to the host star and still be ice-rich.
Too much of a good thing
Interestingly, while we think of water as vital for life, the TRAPPIST-1 planets may have too much water to support life.
“We typically think having liquid water on a planet as a way to start life, since life, as we know it on Earth, is composed mostly of water and requires it to live,” Hinkel explained. “However, a planet that is a water world, or one that doesn't have any surface above the water, does not have the important geochemical or elemental cycles that are absolutely necessary for life.”
Ultimately, this means that while M-dwarf stars, like TRAPPIST-1, are the most common stars in the universe (and while it's likely that there are planets orbiting these stars), the huge amount of water they are likely to have makes them unfavorable for life to exist, especially enough life to create a detectable signal in the atmosphere that can be observed. “It's a classic scenario of ‘too much of a good thing,’” said Hinkel.
So, while we’re unlikely to find evidence of life on the TRAPPIST-1 planets, through this research we may gain a better understanding of how icy planets form and what kinds of stars and planets we should be looking for in our continued search for life.
More Science and technology

ASU-led space telescope is ready to fly
The Star Planet Activity Research CubeSat, or SPARCS, a small space telescope that will monitor the flares and sunspot activity…

ASU at the heart of the state's revitalized microelectronics industry
A stronger local economy, more reliable technology, and a future where our computers and devices do the impossible: that’s the…

Breakthrough copper alloy achieves unprecedented high-temperature performance
A team of researchers from Arizona State University, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Lehigh University and Louisiana State…