Deep freeze puts the squeeze on dwarf planet Ceres
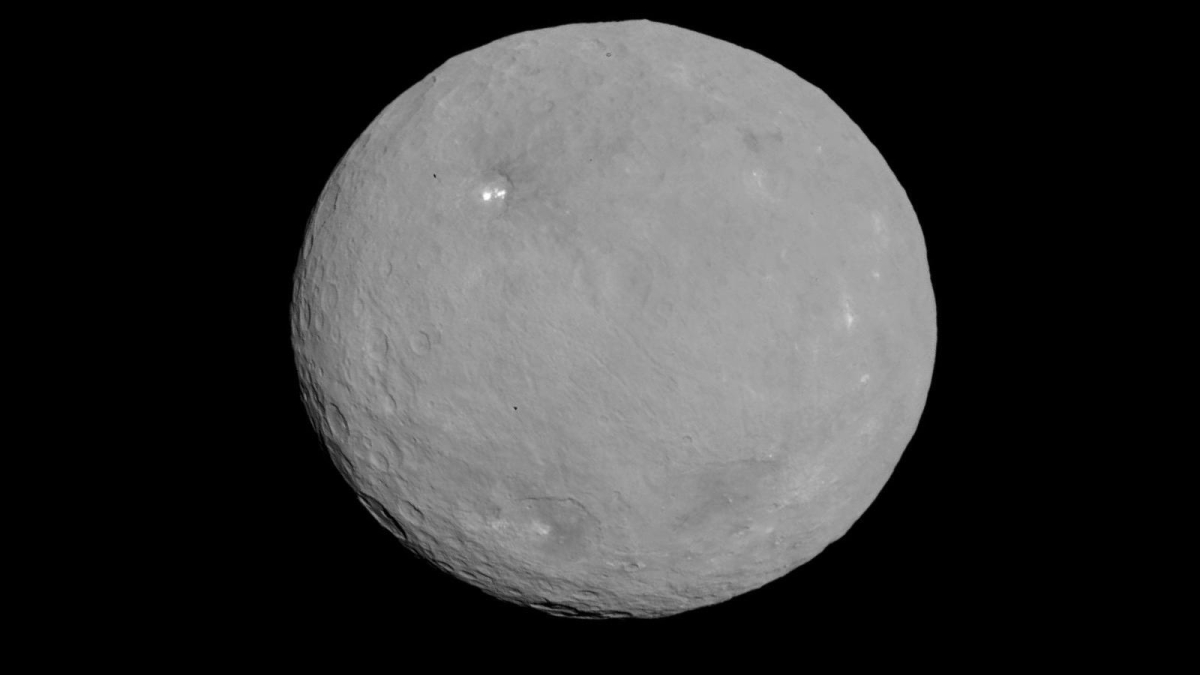

The dark surface of dwarf planet Ceres, seen here in an image from NASA's Dawn mission, shows fresh white spots. ASU researchers Marc Neveu and Steve Desch have an explanation how Ceres gets these puzzling features.
When NASA's Dawn spacecraft approached the dwarf planet Ceres in March this year, scientists and the public alike were intrigued to see that Ceres has an dark, heavily cratered surface with dozens of bright white spots, large and small.
Even more puzzling, the bright spots lie in all kinds of terrain and appear variously as flat patches on the floors of craters and as an isolated peak, in at least one case.
According to Arizona State University's Marc Neveu and Steve Desch, what's emplacing the white material on the surface is what's happening far below. They recently published their model in Geophysical Research Letters to explain what's likely going on.
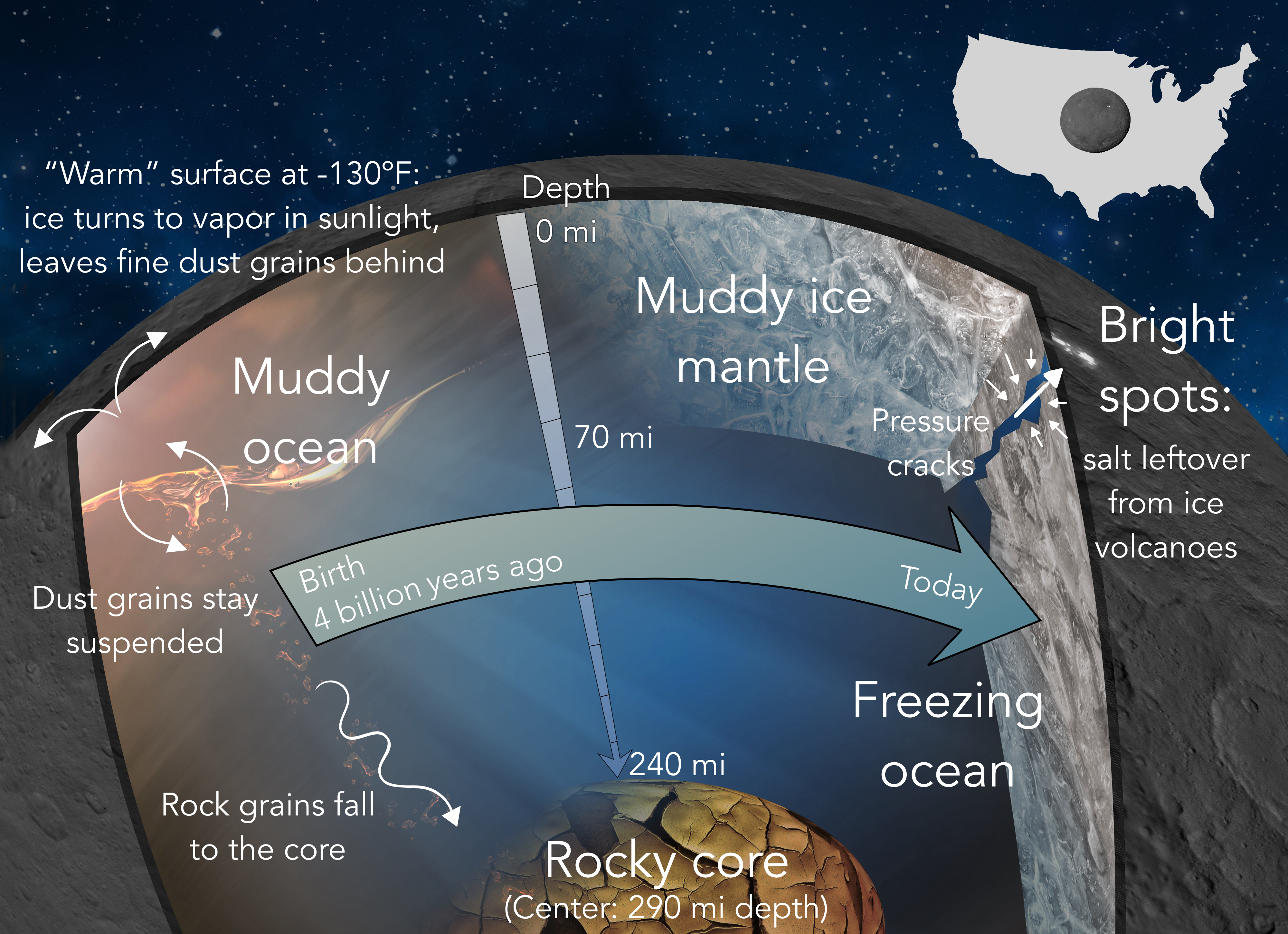
Ceres orbits the Sun in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, at nearly three times Earth's distance from the Sun. Discovered in 1801 and the largest object in the main belt, Ceres is nearly 600 miles wide.
Even before Dawn, scientists knew something was up with Ceres. Earth-based observations and data from orbiting space telescopes had shown it has a surface with water-altered minerals and perhaps a tenuous cloud of water vapor around it.
Dawn's data added to the puzzle. The spots have a brightness that points to ice or salts, and as noted above, they appear as both flat and raised structures in many different types of landscape.
"That was a clue for us," said Neveu of ASU's School of Earth and Space Exploration, where he is a postdoctoral researcher working with Desch, a professor of astrophysics in the school.
"Previously published models suggested that Ceres had subsurface liquid water in the past and possibly until today. We also knew that cryovolcanism on Ceres was definitely an option because a present-day underground ocean would be refreezing and pressurizing liquid water down deep."
Cryovolcanism, or cold volcanism, is partly similar to the ordinary (hot) volcanism that occurs on Earth and other rocky planets. The difference is that in the cryo case, what erupts instead of molten rock is molten ice — liquid water or brine. Water ice would quickly sublimate into the vacuum of space at Ceres' surface, leaving behind salt deposits.
Neveu said the pre-Dawn reports of water vapor were tantalizing clues of surface water or young ice.
"When images released by the Dawn team revealed those bright spots, we immediately thought of a cryovolcanic origin," Neveu said.
Four billion years ago, Ceres formed from a mixture of dust, rocky grains and ices. Today, it has a rocky core under a mantle of ice and rocky fragments. Between the two lie pockets of cold, briny liquid, the source of the white spots on the surface of Ceres. Artwork by Neveu and Desch
Neveu and Desch began with a reasonable assumption that Ceres formed from a mixture of ice and micro-particles of rock and dust. They hypothesized that the rocky particles released heat by radioactive decay. Impacts by meteorites were another likely factor. The heat would melt ice while allowing the denser rock fraction to settle toward the center of Ceres. It would also leave a surface coated with a residue of water-altered minerals.
Said Desch, "Our calculations of Ceres' evolution show that it is just warm enough deep inside Ceres for liquid water to exist." This water, he said, probably has other substances mixed in, making it a brine like seawater. "We calculate a temperature of 240 to 250 Kelvins, or about –27 degrees to –9 degrees Fahrenheit, just warm enough for chloride brines to persist and to be freezing today."
As the brine freezes, Neveu and Desch explained, it will expand (as ice does) and thus raise the pressure on any liquid or briny reservoirs inside Ceres.
"This should drive these fluids up to the surface, where they will erupt as cryovolcanic outflows," according to Neveu.
If cryovolcanism at various places across Ceres’ surface is driven by liquid freezing at depth, this activity may have increased as Ceres has cooled down, making it more likely today.
Cryovolcanism also has a side effect, said Desch: "The eruptions and outflows may contribute to the water vapor being produced at Ceres."
Added Neveu: “Cryovolcanism coming from deep inside Ceres is breathing new activity onto its ancient surface.”
The School of Earth and Space Exploration is a unit in ASU's College of Liberal Arts and Sciences.
More Science and technology

ASU-led Southwest Advanced Prototyping Hub awarded $21.3M for 2nd year of funding for microelectronics projects
The Southwest Advanced Prototyping (SWAP) Hub, led by Arizona State University, has been awarded $21.3 million in Year 2 funding…

Celebrating '20 Years of Discovery' at the Biodesign Institute
Editor’s note: The Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University wraps up its 20th anniversary with the sixth and final…

Student research supports semiconductor sustainability
As microelectronics have become an increasingly essential part of modern society, greenhouse gas emissions, which are associated…