Fuel for thought: Advancing solar-to-fuel technology

The artificial photosynthesis device highlighted in the new study pairs a semiconductor component with a catalytic material that can speed up the rate of chemical reactions. Sunlight is harvested by the light-gathering semiconductor and used to power the catalytic component, which drives chemical reactions that produce clean fuel — in this case, hydrogen. Graphic by Jason Drees
As heat waves, floods and wildfires rage and world leaders fret, the climate crisis intensifies.
To date, humans have managed only tentative steps to reduce the output of heat-trapping carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Breaking the impasse of fossil fuel addiction will require bold new technologies, as well as foundational changes to both public and private policymaking.
In new research, Gary Moore and his research group describe technology engineered to convert radiant energy from the sun into so-called solar fuels, which can be stored or used as carbon-neutral or carbon-free sources of energy to help power the modern world.
Although this suite of emerging technologies is still in a formative phase, considerable progress has brought the idea closer to reality.
“It's likely that fuels will be part of our energy infrastructure for the foreseeable future, particularly for long-haul transportation, including air travel. These require dense sources of energy,” Moore says. “If we're serious about stabilizing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, we need to radically adjust our current energy portfolio.”
In a letter appearing in the journal ACS Applied Energy Materials as a cover article, authors Nghi P. Nguyen, Lillian K. Hensleigh, Daiki Nishiori and Edgar A. Reyes join Moore in describing techniques for testing and repairing solar fuel-generating devices. All are researchers in Arizona State University's Biodesign Center for Applied Structural Discovery and the ASU School of Molecular Sciences.
“The types of technologies that Nghi, Lillian, Daiki and Edgar are advancing hold promise for leveraging an existing infrastructure that uses fuels but reimagines the chemistry of an entire industry to be more sustainable,” Moore says.
A page from nature
Among solar-to-fuel technology variants are devices that mimic natural processes of plants and other photosynthetic organisms. Here, light energy from the sun is transformed into energy stored in chemical bonds, later released during respiration, and used to power cellular activities.
The artificial photosynthesis device highlighted in the new study pairs a semiconductor component with a catalytic material that can speed up the rate of chemical reactions.
Sunlight is harvested by the light-gathering semiconductor and used to power the catalytic component, which drives chemical reactions that produce clean fuel — in this case, hydrogen.
The technology holds significant promise for the future of sustainable energy, once issues of energy efficiency, cost effectiveness and operational durability have been resolved.
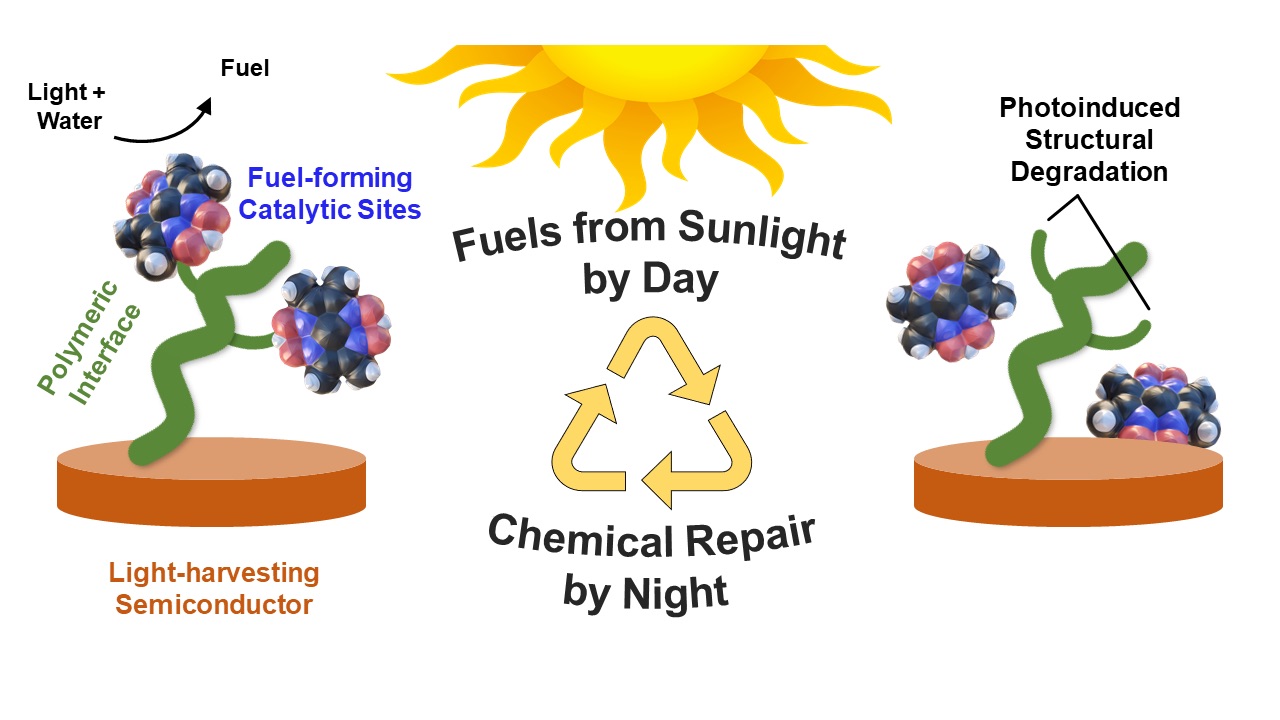
Circular chemistry: Moore and coworkers are developing polymer-based surface coatings that integrate the solar-energy-harvesting properties of semiconductors with molecules that provide low-energy pathways for producing non-fossil-based fuels domestically. Their recent discoveries show these coatings also enable reassembly of fuel-forming components that can detach during operation, establishing a degrade-repair cycle.
Forging new bonds
The current research addresses a well-known phenomenon: the degradation over time of the catalytic components of such devices during solar fuel production. Using advanced spectroscopic methods, the researchers characterize the bond-breaking stages that result in performance degradation over time.
"Our report describes a general but useful approach for better understanding the structure-function relationships governing the performance of molecular-modified photoelectrodes," Nguyen says.
Having analyzed the chemistry involved in producing this degradation, they next describe a means of mending the damaged chemical structure and restoring performance. The group has been working for some time to improve the materials involved, including the application of new polymer coatings to the light-absorbing semiconductor, enhancing the hydrogen-producing performance of such devices. The coatings also provide a scaffold that can be used to repair catalytic components degraded during operational use.
“Characterizing the structural changes accompanying the degradation in rates of fuel production enables durability studies that go beyond just observing changes in performance over time," Hensleigh says.
Paths out of the CO2 labyrinth
With the ability to repair degraded catalysts and restore their function, such technology could conceivably operate to produce essential fuels by day while using nighttime hours for structural repair, extending the life cycle of these materials.
“This changes the paradigm for how we use these materials, transitioning from linear, single-use approaches to processes that adapt circular chemistry and materials that are recyclable and/or reusable,” Moore says.
Gary Moore is a researcher in ASU's Biodesign Center for Applied Structural Discovery and the School of Molecular Sciences.
In addition to hydrogen, the innovative technologies could produce a variety of liquid fuels that are either carbon-free or -neutral, in the latter case, reusing the carbon produced to power new reactions in a closed loop of chemical activity in which no new CO2 is produced.
Advances in related materials will also promote carbon-capture technologies, which will likely be needed to remove existing CO2 from the atmosphere, given the scale of the climate dilemma.
“We are at a tipping point in terms of balancing the Earth’s planetary cycles and recourses,” Moore says. “Looking to the future, if we're serious about correcting this, we need to make larger investments in research activities and policies that support an energy infrastructure that is not reliant on fossil-based fuels.”
In recognition of Moore’s pioneering research into clean energy technologies, he was recently awarded the 2023 Inter-American Photochemical Society's Young Investigator Award.
More Science and technology
Extreme HGTV: Students to learn how to design habitats for living, working in space
Architecture students at Arizona State University already learn how to design spaces for many kinds of environments, and now they…

Human brains teach AI new skills
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is rapidly advancing, but it hasn’t yet outpaced human intelligence. Our brains’ capacity for…

Doctoral students cruise into roles as computer engineering innovators
Raha Moraffah is grateful for her experiences as a doctoral student in the School of Computing and Augmented Intelligence, part…