Researchers discover the catalyst 'holy grail'
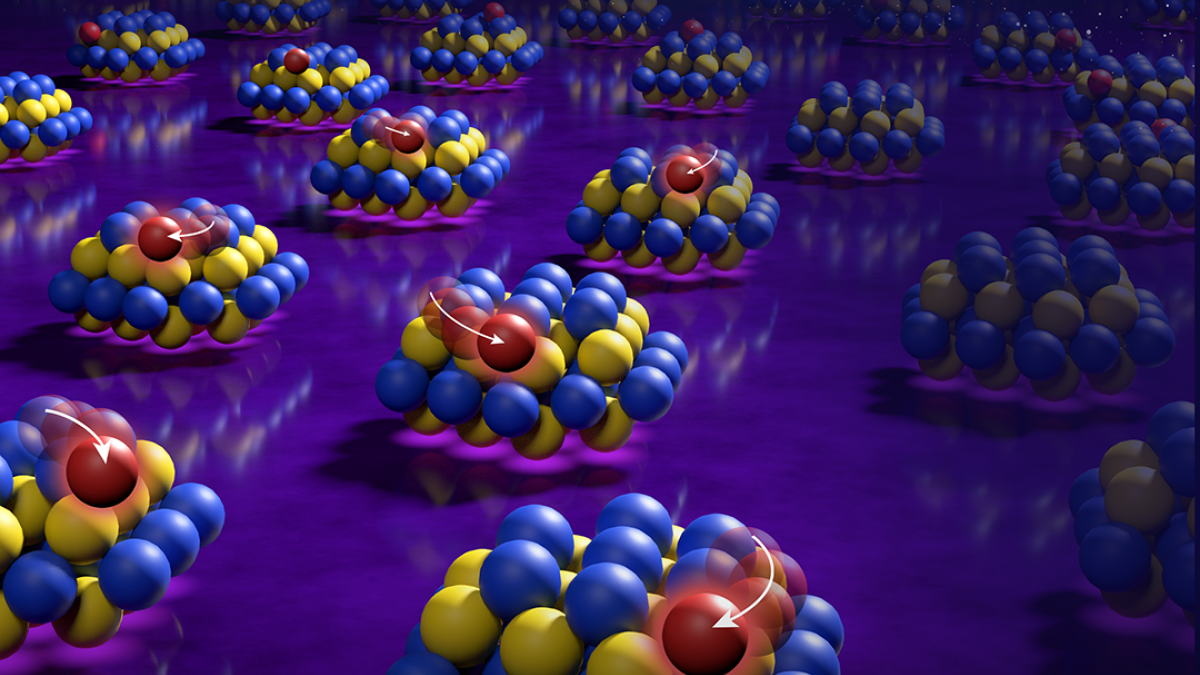
The researchers confined platinum-group atoms to small cerium-oxide islands, which could minimize the amount of expensive metals required in many industrial applications. Image courtesy Mike Perkins/Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Catalysts, which speed up chemical reactions, are key to the technologies used in making chemicals and fuels and for cleaning up pollutants, including exhaust from cars, trucks and fossil fuel power plants. Many catalysts contain precious metals such as platinum, rhodium and palladium, which are extremely expensive.
A new method, published in Nature on Oct. 26, anchors single atoms of platinum-group metals on nanometer-sized islands in order to more efficiently use these expensive metals as catalysts.
Researchers in the early 1990s began investigating how to isolate metal atoms as catalysts, but they hadn’t been able to stabilize them at the high temperatures required for catalytic converters and other practical applications. Once the metal atoms are exposed to the conditions required for reactions, they tend to clump together.
Arizona State University physics Professor Jingyue Liu; Bruce Gates, of University of California, Davis; Yong Wang, of Washington State University; and their research team solved this problem by dispersing the metal atoms within nanometer-sized islands of cerium oxide on a commercial silicon dioxide support.
With its extremely high surface area, the silicon dioxide is able to anchor a large number of the islands, which hold the metal atoms within a small volume. The cerium oxide sticks like a glue to the silicon dioxide and holds the individual metal atoms tightly so that they don’t wander off to find each other, clump and become ineffective.
“The stabilization of precious metals to allow each atom to be a catalyst is a holy grail in the catalysis field,” Wang said. “We are not only using the least amount of platinum group metals but are also making each atom much more reactive.”
The researchers found that the island-confined metal atoms were stable in catalyzing reactions under both oxidative and reductive conditions. Oxidation, in which oxygen is added to a substance, is used in emission control technology to remove harmful carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons, whereas reduction, in which hydrogen is present and reacts with other molecules, is used for many industrial applications to produce fuels, fertilizers and drugs.
“The atomic precision of the manufacture of the new catalysts may open avenues to design catalysts with unprecedented flexibility in the placement of targeted numbers of atoms on each island,” Gates said. “That allows us to investigate the reactivity and identify the most reactive species — to find out which structures and configurations are most efficient.”
The researchers hope to further study the approach for a wide range of catalytic applications.
“This work gives the scientific community a new tool in the toolkit to understand the catalytic site requirement for specific reactions of interest and for developing highly active and stable new catalysts,” Liu said. “It creates tremendous opportunities for catalytic technology and takes atomically dispersed metal catalysts one major step closer to practical applications.”
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation’s Division of Chemistry and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Basic Energy Sciences Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences within the Catalysis Science Program.
More Science and technology

Cracking the code of online computer science clubs
Experts believe that involvement in college clubs and organizations increases student retention and helps learners build valuable…
Consortium for Science, Policy & Outcomes celebrates 25 years
For Arizona State University's Consortium for Science, Policy & Outcomes (CSPO), recognizing the past is just as important as…

Hacking satellites to fix our oceans and shoot for the stars
By Preesha KumarFrom memory foam mattresses to the camera and GPS navigation on our phones, technology that was developed for…