New Fulton Schools master’s degree program focuses on robotics, autonomous systems

The members of ASU’s Interactive Robotics Lab have been exploring human-robot interaction and collaboration through the development of machine learning methods that allow humanoid robots to behave in an intelligent and autonomous manner. Photo by Bailey Vidler/ASU
The age of robotics and autonomous systems is upon us. These emerging technologies have the potential to increase the efficiency, productivity and safety of humans in manufacturing, transportation, aerospace, defense, health care and many other critical fields.
Within the last five years, these fields have seen tremendous growth. Despite that, industry and academia are in pressing need of qualified personnel to continue pursuing advancements in robotics and autonomous systems to positively affect people, the planet and future generations.
As a result, Arizona State University’s Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering has created a new master’s degree program in robotics and autonomous systems designed to train the next generation of robotics researchers with multidisciplinary knowledge in artificial intelligence, computer science, machine learning, sensing and signal processing, mechanical engineering and a variety of other advanced topics.
“In the future, we’re going to be interacting with intelligent machines a lot in our everyday lives,” said Panagiotis Artemiadis, the robotics and autonomous systems graduate program chair and an associate professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering. “We need to make sure people understand how to design, build and control the intelligent machines that will ultimately make our lives easier.”
ASU’s new graduate program, which launched Jan. 7, is one of fewer than 10 in the country specialized in the field of robotics and autonomous systems. Students will gain in-depth theoretical knowledge and practical experience working across engineering specialties — such as mechanical systems, electrical systems, computation and intelligence — to develop and control robotic platforms and autonomous systems geared toward improving quality of life for all.
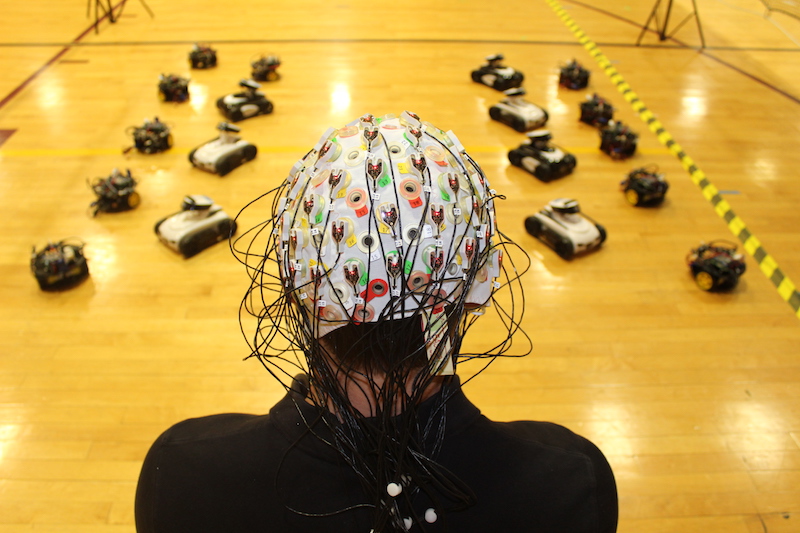

Associate Professor Panagiotis Artemiadis, the director of ASU’s Human-Oriented Robotics and Control Laboratory, has been working on understanding how humans can perceive and control collective behaviors for a swarm of semi-autonomous agents. Photo courtesy of Panagiotis Artemiadis
The Master of Science program is a collaboration between four of the six Fulton Schools: The Polytechnic School; the School for Engineering of Matter, Transport and Energy; the School of Computing, Informatics, and Decision Systems Engineering; and the School of Electrical, Computer and Energy Engineering.
“We created the program because we need to train more people to overcome the current shortage of qualified personnel within robotics and autonomous systems,” said Lina Karam, a professor of electrical engineering in the Fulton Schools. “Students need a breadth of knowledge to create the next generation of technologies that can have a significant impact on our economy and quality of life.”
Alex Goldman, who received a mechanical engineering degree from the University of Michigan, was drawn to the graduate program because of its focus on interdisciplinary collaboration.
As part of the first cohort of students in the program, Goldman will specialize in aerospace and mechanical engineering, but he is also excited about the ability to choose from the program’s large number of courses in other disciplines — ranging from advanced system modeling and mechatronics device innovation to computer-controlled systems and human-aware robotics.
Goldman also wants to conduct research at the intersection of robotics and water. In one of his courses, he’ll work with a doctoral student who is designing an autonomous vehicle to detect microplastics in Tempe Town Lake near ASU's Tempe campus. He’s also excited to collaborate with professors who are designing octopus-inspired autonomous arms and autonomous water vehicles.
“I find people get really excited about space exploration, but we know more about the surfaces of several other planets than we do our ocean floor,” said Goldman, whose interest in water research spurred from his passion for scuba diving. “It’s a frontier of exploration for me. I want to help conserve our oceans so the next generations can continue to enjoy everything I’ve enjoyed.”
Students like Goldman will have the opportunity to work with leading researchers in more than 20 world-class robotics labs in areas fit for their unique research interests, such as autonomous vehicles, biologically inspired mechatronic technologies, household robotics, multi-agent systems, robot-aided neurorehabilitation, soft robotics, swarm robotics, unmanned vehicles and wearable assistive devices.
Many of the robotics labs also have strong ties to industry partners and collaborators, which enable graduate students to interact with and present their ideas to industry representatives.
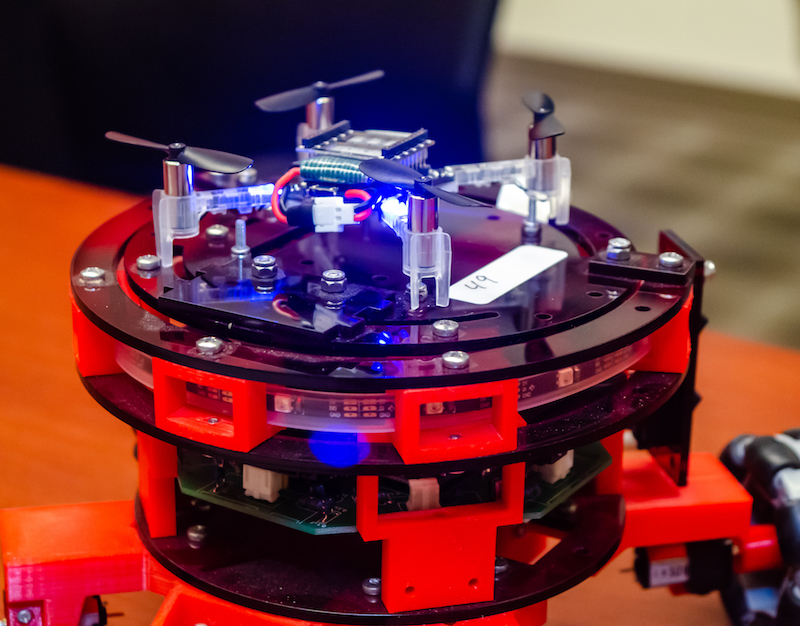
ASU Associate Professor Spring Berman directs the Autonomous Collective Systems Laboratory, where researchers design and control ground and aerial robotic platforms. Photo by Bailey Vidler/ASU
“We cover most if not all the areas of robotics,” said Georgios Fainekos, an associate professor of computer science and engineering in the Fulton Schools. “You can be embedded into a lab of your choice and make progress in your career.”
The new master’s degree program — which has already received more than 200 applications since opening on Nov. 14, 2018 — is just one initiative of many that are working toward effectively utilizing the university’s expansive multidisciplinary research community to expand its impact in the age of robotics and autonomous systems.
“I’m really excited to be a part of the first class of people getting into the program and being a part of what I think will be a much bigger program pretty soon,” said Goldman.
More Science and technology

How one professor re-creates the extreme interiors of planets in an ASU lab
Despite decades of research, we may not understand the Earth as well as we think.In grade school, we learn about the planet’s…

DNA provides a solution to our enormous data storage problem
Since the dawn of the computer age, researchers have wrestled with two persistent challenges: how to store ever-increasing reams…

Why middle-aged Americans are falling behind peers abroad in various health measures
Americans born in the 1960s and early 1970s report higher loneliness and depressive symptoms, and show poorer memory and physical…