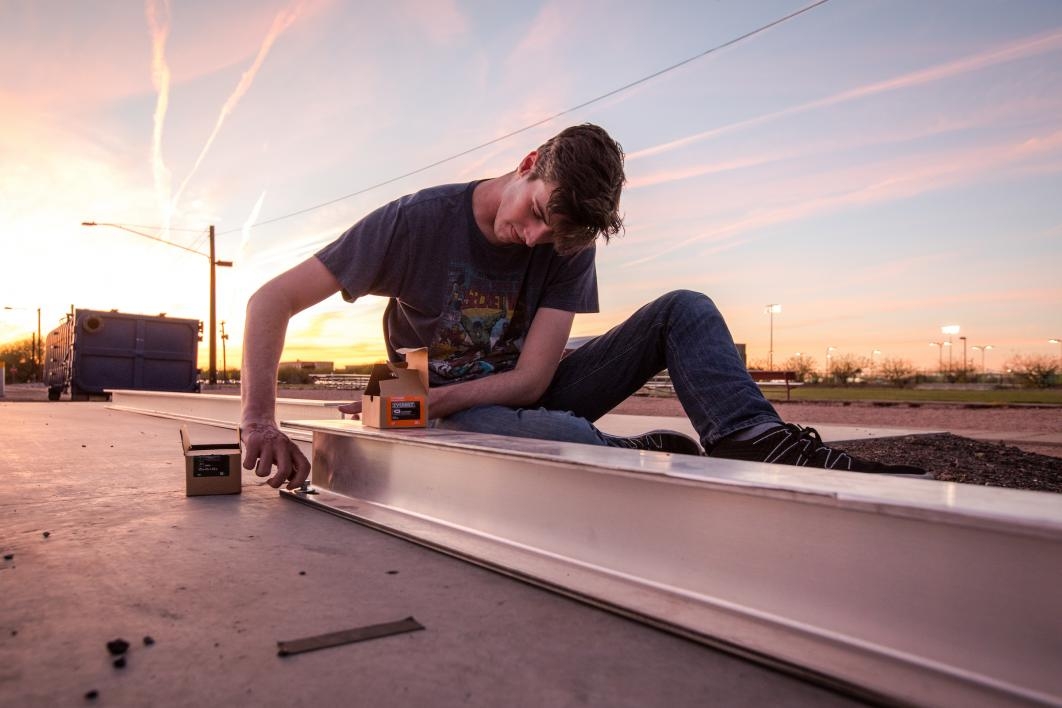
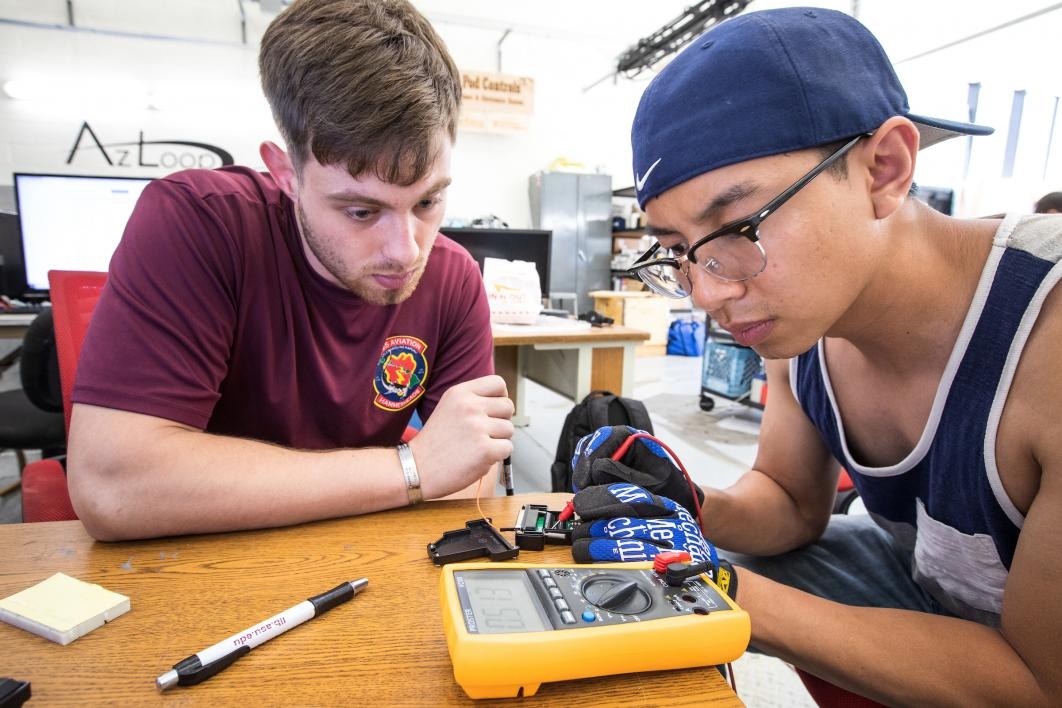
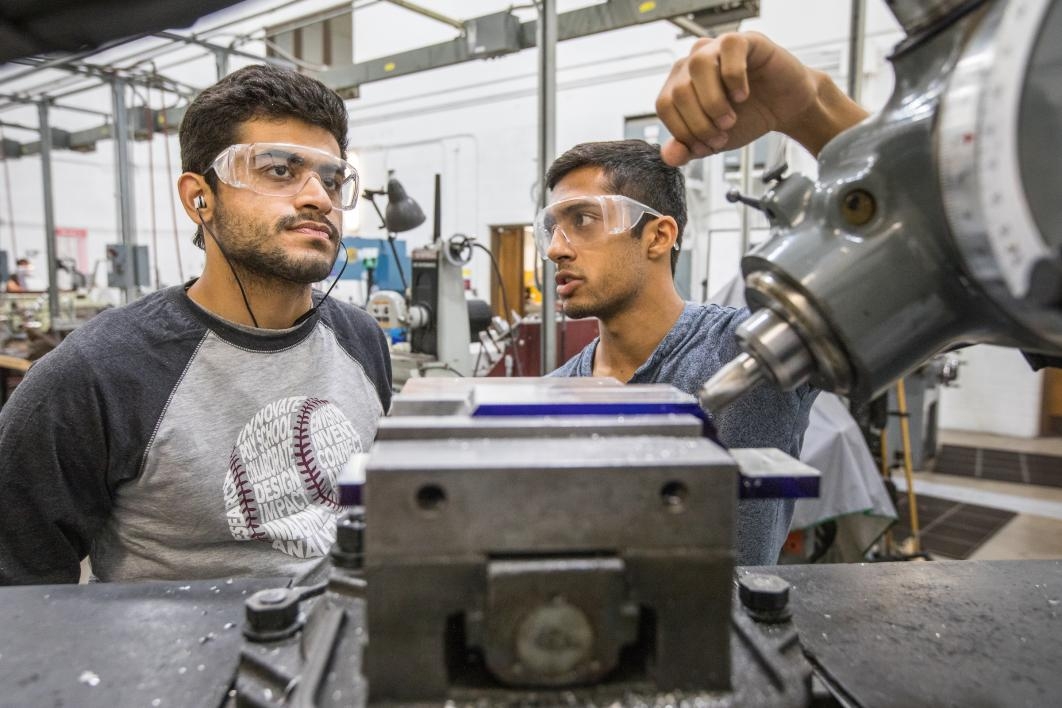
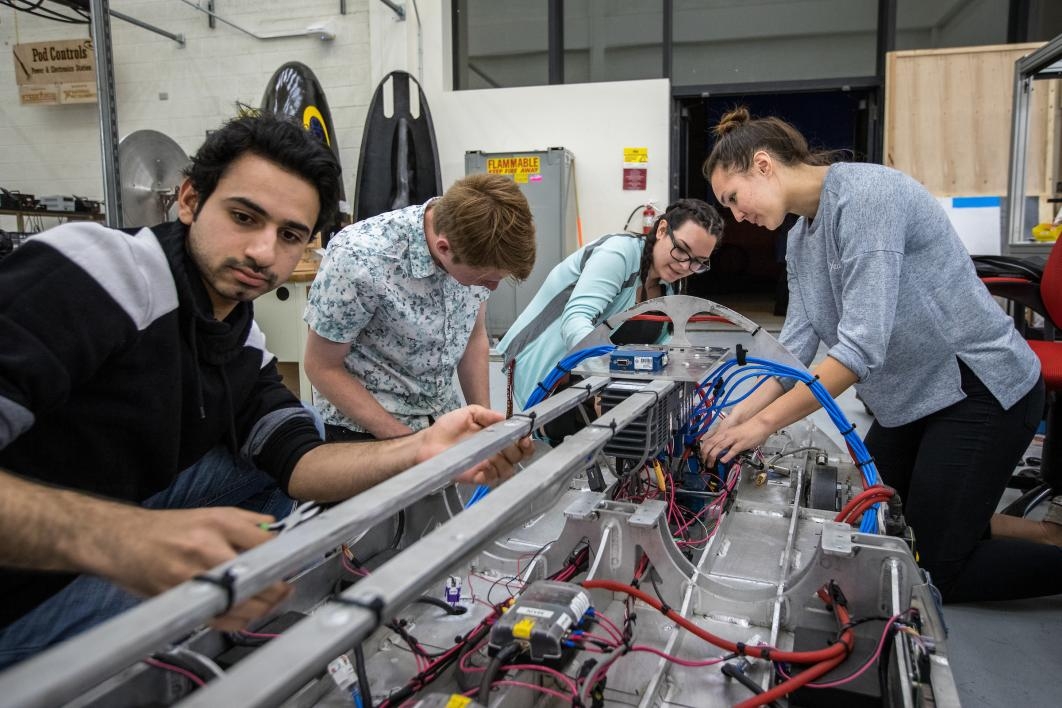
High-speed transportation technology for hyperloop seemed like a good first step for an Arizona State University mechanical engineering student who someday wants to help colonize the galaxy.
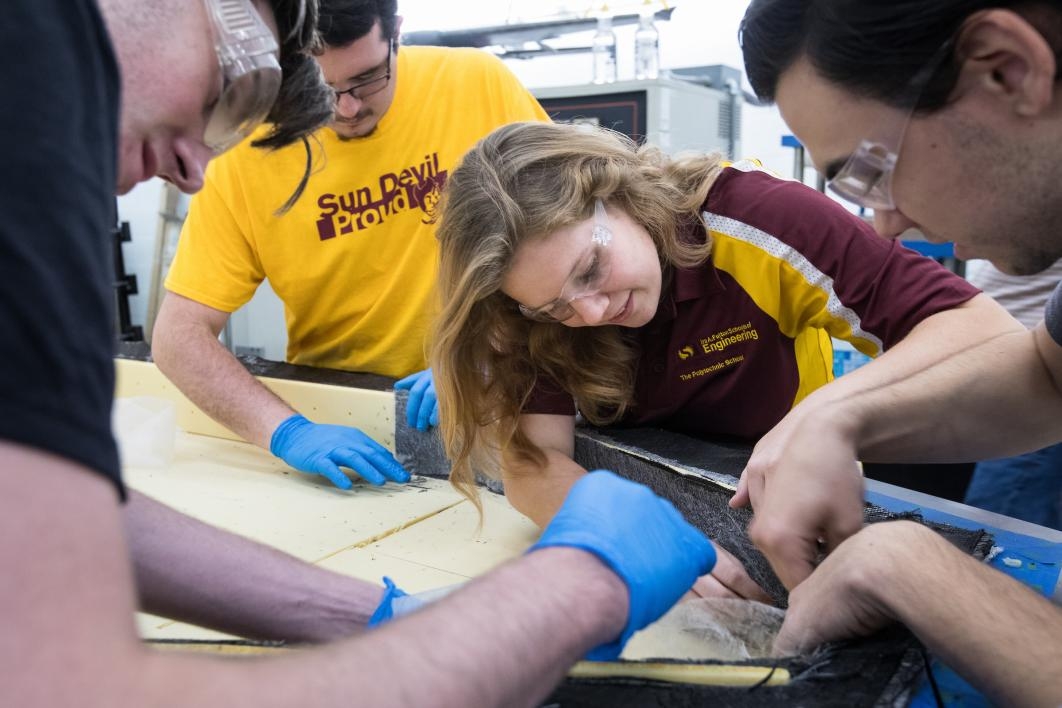
Leann Scott, who will graduate next spring after just three years of school and who will spend her fourth year as a master’s degree student, joined ASU’s AZLoop hyperloop team last year as a member of the propulsion team. This year, she wanted to move into manufacturing and was elected to be that team’s lead.
A longtime Star Trek fan, Scott believes that “the final frontier” will involve putting people on other planets, and that hyperloop technologies can help get them there.
“The next phase of rocket and aircraft construction will switch from aluminum to composites like carbon fiber and fiberglass — exactly the kinds of materials we’re working with for hyperloop design,” Scott said.
Hyperloop is a conceptual high-speed transportation system that would use pressurized tubes to send passenger pods between cities at speeds up to 700 miles per hour. AZLoop will head to SpaceX in Hawthorne, California, next week to compete their design against nearly 20 other collegiate teams.
For this year’s competition entry, the manufacturing team wanted to minimize weight and add stiffness to the chassis and pod designs with more extensive use of lightweight carbon fiber, but didn’t have the needed expertise. Josh Bowen, the AZLoop president, told Scott that if she needed outside expertise, she’d have to go out and find it.
She reached out to Composites One, a leading composites distributor in the aerospace and transportation industries. Two weeks later, the company sent a technical expert from its Southern California office to work with AZLoop on design and processing strategies, a commitment that has continued for five additional trips. Two engineers from the Phoenix office are regular advisers during the team’s Friday-night work sessions. “(They're) both here getting their hands dirty and making sure we don’t mess it up,” said Scott with a laugh.
“Our entire team learned resin infusion techniques,” she said. “Composites One helped us create prototypes and build practice molds, working with us to figure out how the battery box, electrical wiring and propulsion components would fit into the design.
“These problem-solving and implementation experiences will give us a major advantage when we hit the job market.”
Video by Ken Fagan/ASU Now
A third-generation engineer — both her parents are electrical engineers and her grandfather was a chemical engineer — Scott said she was taught from an early age to look at a problem and figure out how to proceed: “When I was 6, our Slip 'N Slide was missing a part, so I figured out how to make it work by connecting the hose to the slide using duct tape and a funnel.”
Scott graduated from Perry High School in Gilbert, Arizona, and said being the oldest of three siblings gave her some good team-management skills, as does guidance from her father, a team manager at Intel.
But Scott also credits teammate Pamela Lombardi, a former Marine, with helping keep the team on track. A robotics senior who served as a helicopter mechanic while in the service, Lombardi also has been invaluable in troubleshooting circuit, mechanical and wiring systems.
“I think both of us can be pretty intimidating,” said Lombardi. “Together, we’ve been pretty successful at getting the team to listen.”
The team’s next goal is to test all systems in the assembled pod on the 150-foot track and in the 25-foot pressure chamber on ASUs Polytechnic Campus. One other U.S. team has a track, but it's only 50 feet long — too short to test braking systems. AZLoop is the only U.S. team that has a pressure chamber.
"The facilities at ASU give our team a tremendous advantage as we head to Hawthorne," said Scott.
Scott remains resolute that her work on hyperloop is a fast track to space.
“Humanity’s efforts in space have taught us about water purification, climate change and, by studying astronauts when they return to Earth, osteoporosis and disease immunity. Technological advances happen when we’re focused on exploring.”
SpaceX hyperloop competition
Originally introduced in 2012 by founder Elon Musk, SpaceX is hosting the third annual collegiate competition in Hawthorne, California. ASU’s team, which completed all of the safety and operation tests in last year’s competition and ranked as a top-rated team, is one of 11 U.S. teams out of 18 overall vying for a finalist spot in the tube.
Since 2012, proposed routes from Toronto to Montreal, Chicago to Columbus to Pittsburgh, and Abu Dhabi to Dubai, among others, are in development. Virgin Hyperloop One has a full-scale, 500-meter test track, known as DevLoop, in the Nevada desert.
AZLoop Pod Unveiling
What: AZLoop will display its 2018 competition pod for students, faculty and the general public.
When: 6 p.m. Monday, July 9.
Where: ASU Student Pavilion, 400 E. Orange St., Tempe.
Details: Registration requested.
Top photo: AZLoop team members Leann Scott (left) and Pamela Lombardi tack on foam guides to the base of the carbon-fiber chassis at ASU's Polytechnic campus on June 22. With the system design plans finished and all the parts ordered, the group of ASU students, with support from Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, will take the vehicle to Southern California for the July 2018 SpaceX hyperloop competition. Photo by Charlie Leight/ASU Now
More Science and technology

ASU and Deca Technologies selected to lead $100M SHIELD USA project to strengthen U.S. semiconductor packaging capabilities
The National Institute of Standards and Technology — part of the U.S. Department of Commerce — announced today that it plans to award as much as $100 million to Arizona State University and Deca…
From food crops to cancer clinics: Lessons in extermination resistance
Just as crop-devouring insects evolve to resist pesticides, cancer cells can increase their lethality by developing resistance to treatment. In fact, most deaths from cancer are caused by the…

ASU professor wins NIH Director’s New Innovator Award for research linking gene function to brain structure
Life experiences alter us in many ways, including how we act and our mental and physical health. What we go through can even change how our genes work, how the instructions coded into our DNA are…