Sinking ground in San Francisco Bay will worsen flooding from rising sea levels

New research shows that sections of the San Francisco Bay shoreline are sinking at rates of nearly half an inch (10 millimeters) a year.
But knowledge of where the ground in the Bay Area is sinking, and by how much, is not included in the official planning maps that authorities use to assess the local flooding risk from rising sea levels.
The new findings appear in a paper published March 7 in the journal Science Advances. The lead author is Manoochehr Shirzaei, assistant professor in Arizona State University's School of Earth and Space Exploration and a member of NASA's Sea Level Change planning team. His co-author is Roland Bürgmann of the University of California, Berkeley.
The scientists measured how much the land along the bay's shoreline has sunk with interferometric imaging using synthetic aperture radar from Earth orbit to detect elevation. The technique is sensitive enough to measure year-to-year changes in local ground elevation as small as a millimeter. Their study used data from 2007 to 2011.
"Although we found that most of the bay's shoreline is sinking by less than 2 millimeters a year, in several areas we discovered subsidence rates of 10 millimeters a year and more," Shirzaei said.
He points to San Francisco Bay's Treasure Island as an example of land that is subsiding at a relatively high rate. The island, located in the bay midway between San Francisco and Oakland, was created as landfill for the 1939 Golden Gate International Exposition, but is now mostly a mix of historic buildings. The northwest corner of Treasure Island is sinking at a rate of half an inch to three-quarters of an inch (13 to 19 millimeters) a year.
It is, the scientists said, typical of most areas of land subsidence in the Bay Area. Many are former landfills that are slowly compacting, while others are places where streams and rivers are depositing successive layers of mud as they flow into the bay.
Not on FEMA's planning maps
The scientists note that state, county, and municipal administrations currently use maps prepared by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to make plans for dealing with possible flooding.
FEMA's Increased Flooding Scenario Maps brochure and FAQ use data from the agency's San Francisco Bay Area Coastal Study to estimate how the coastal floodplain would change with a 1-foot, 2-foot, and 3-foot rise in bay water levels.
When Shirzaei and Bürgmann examined different sea-level rise scenarios, they found that for the San Francisco Bay shoreline by the year 2100, some 20 to 160 square miles (52 to 414 square kilometers) face a risk of flooding.
But that was just from rising sea levels. When they added the effects of sinking ground along the shoreline, they found the area threatened by rising water was notably larger: 48 to 166 square miles (124 to 430 square kilometers).
"There are many estimates and models for sea-level rise," Shirzaei said, "but they all fall short because they don't take into account land elevation changes."
These estimates are conservative, the researchers add. Extreme high tides, major storms and periods of high runoff from rain and snowmelt in the rivers that feed into the bay can raise its water level temporarily above that projected from rising sea levels.
“Flooding from sea level rise is clearly an issue in many coastal urban areas,” co-author Bürgmann said. “This kind of analysis is probably going to be relevant around the world, and could be expanded to a much, much larger scale."
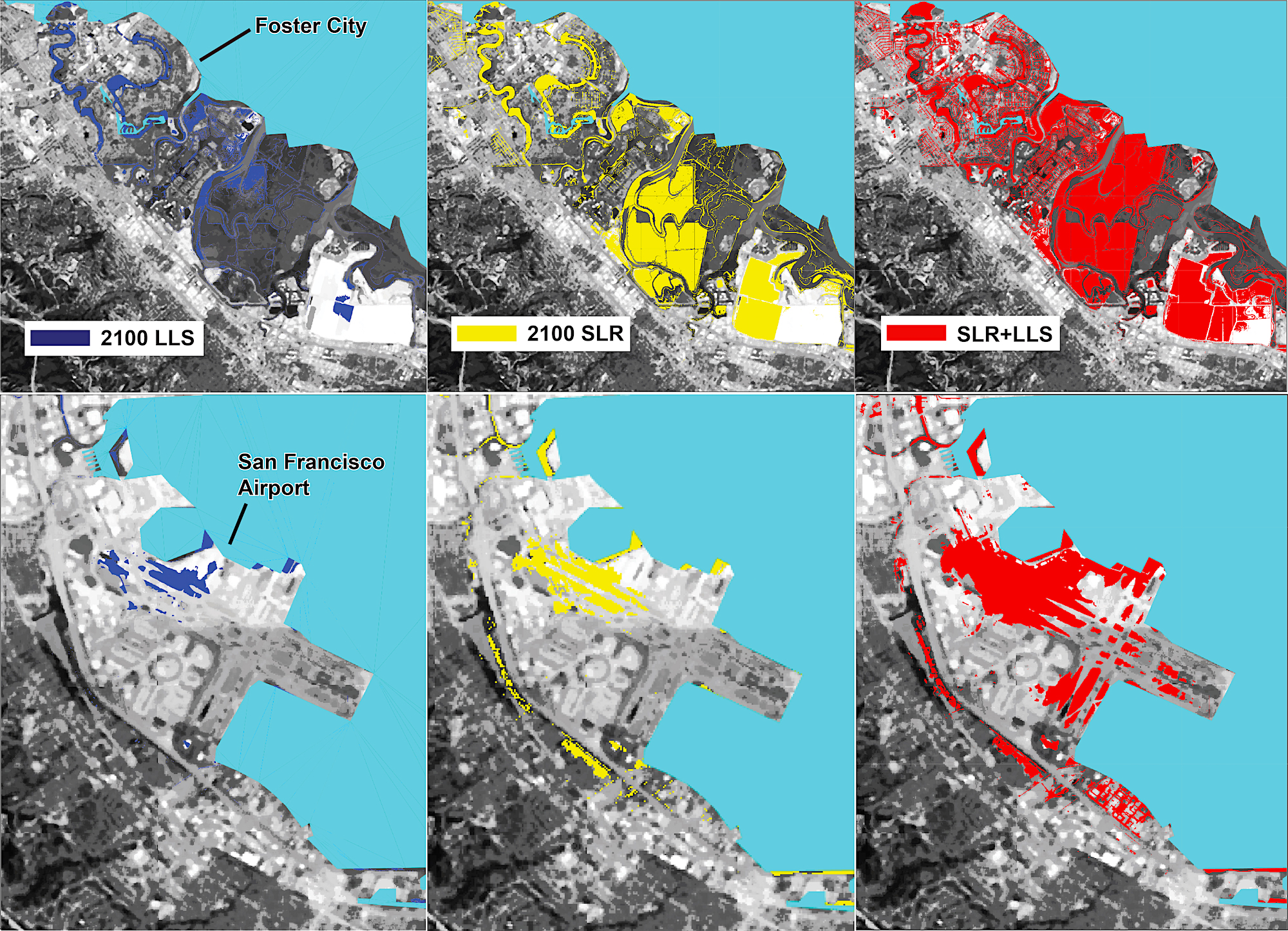
Foster City and San Francisco International Airport both have high economic value combined with heightened risk from flooding by 2100. Areas in dark blue indicate where the local land is sinking (LLS), yellow shows what is at risk from sea-level rise (SLR), and areas in red show the impact of both processes combined. Image by Manoochehr Shirzaei/ASU
High economic impact
When formerly dry land becomes flooded, it causes saltwater contamination of surface and underground water and it accelerates coastal erosion and wetland losses.
But the scientists spotlight two areas of sinking ground on the bay's shoreline where flooding would have a high economic impact: San Francisco International Airport and Foster City.
The airport, built mostly on landfill, handles more than 200,000 annual landings and sees 56 million passengers passing through it each year. The airport is both a destination for travelers to the Bay Area and a hub for domestic and international flights. The scientists' data show that when land subsidence is combined with projected rising sea levels, water will cover nearly half the airport's runways and taxiways by the year 2100.
Foster City, which lies halfway between San Francisco and San Jose, was built in the 1960s, partly on engineered landfill. It has become home to a growing number of high-tech and IT companies because real estate is limited and expensive in the Bay Area to the north and south. However, the parts of the city that were built on landfill are subsiding and, coupled with rising sea levels, significant parts of the city will be at risk of flooding by 2100.
Looking forward
The researchers note that the FEMA maps of the Bay Area need to be updated with the measurements of land subsidence as well as recent projections of rising sea level so that local authorities can make better flood resilience plans.
Unfortunately, Shirzaei said, sinking ground along the shoreline greatly magnifies the effects of sea level rise because the processes work together to worsen the situation.
"The ground goes down, sea level comes up, and floodwaters go much farther inland than either change would produce by itself."
Top photo: San Francisco International Airport is one of several high-economic-impact areas along the shoreline of San Francisco Bay that are at doubled risk of flooding. In addition to the threat from rising sea level, the ground itself is sinking as the landfill it was built on becomes compacted with age. Image courtesy of Calbookaddict at English Wikipedia
More Science and technology

Cracking the code of online computer science clubs
Experts believe that involvement in college clubs and organizations increases student retention and helps learners build valuable social relationships. There are tons of such clubs on ASU's campuses…
Consortium for Science, Policy & Outcomes celebrates 25 years
For Arizona State University's Consortium for Science, Policy & Outcomes (CSPO), recognizing the past is just as important as designing the future. The consortium marked 25 years in Washington, D…

Hacking satellites to fix our oceans and shoot for the stars
By Preesha KumarFrom memory foam mattresses to the camera and GPS navigation on our phones, technology that was developed for space applications enhances our everyday lives on Earth. In fact, Chris…